110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MicroRNA 在葡萄膜黑色素瘤中的作用综述
Authors Li YF, Dong L, Li Y, Wei WB
Received 14 March 2020
Accepted for publication 12 June 2020
Published 1 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 6351—6359
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S253946
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
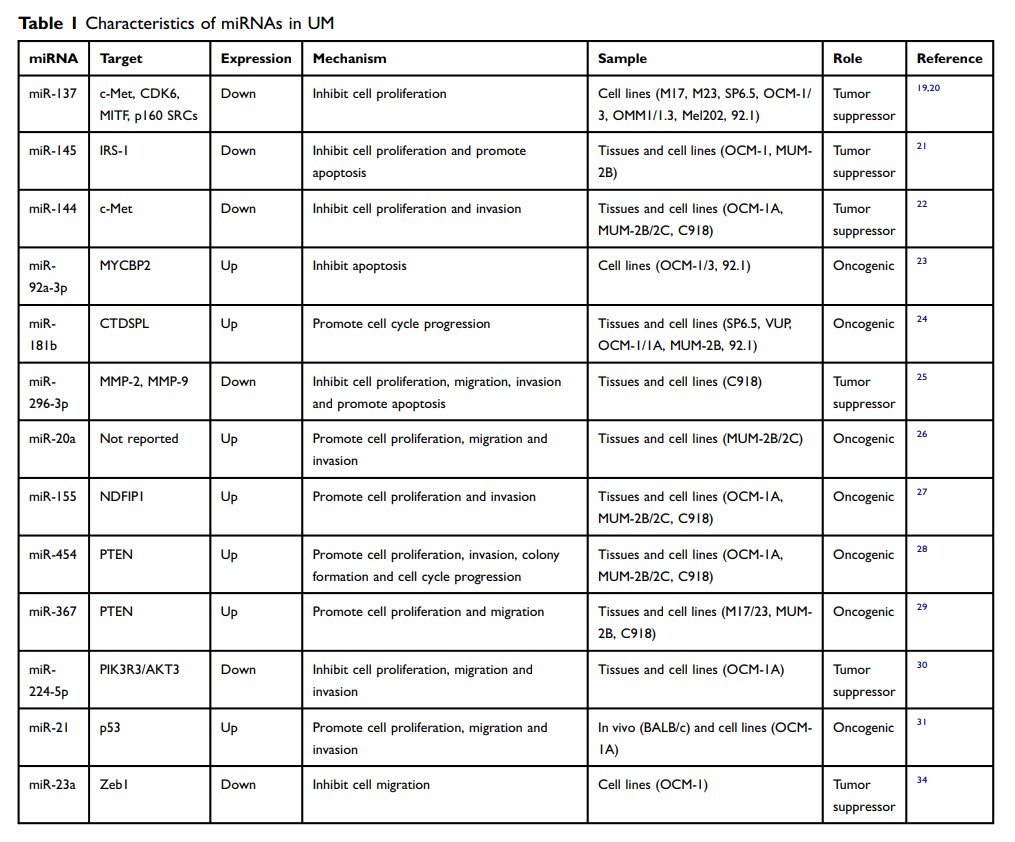
Abstract: Uveal melanoma (UM) is the most common and aggressive primary intraocular tumor in adults. UM is classified as a malignant tumor with a strong tendency of metastasis, which always leads to poor outcomes. At present, the pathogenesis of UM remains unclear and lacks effective therapies. Recent studies have shown that microRNAs (miRNAs), defined as a group of 21– 23 nucleotides single-stranded noncoding RNAs, play a significant role in UM. By binding to the complementary sites within the 3ʹ untranslated region (3ʹUTR) of message RNAs (mRNAs), miRNAs regulate genes by decaying mRNAs or inhibiting their translation. Thus, miRNAs can modulate various biological behaviors of tumors, including cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis. Furthermore, miRNAs have shown clinical applications by serving as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis, regulating immune response, and functioning as epigenetic regulators. It is reasonable to believe that miRNAs have wide application prospects in the early diagnosis and therapy of UM.
Keywords: uveal melanoma, microRNA, biomarker, immune response, review