110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

湖北省 16 城市中严重急性呼吸系统综合征冠状病毒 2(SARS-CoV-2)的传播趋势动态
Authors Fawad M, Mubarik S, Malik SS, Hao Y, Yu C, Ren J
Received 20 March 2020
Accepted for publication 11 June 2020
Published 2 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 699—709
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S254806
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Professor Henrik Toft Sørensen
Objective: A severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was detected by researchers from a patient in Wuhan, Hubei province, China, in December 2019, and broke out in January 2020. Then, the pandemic was detected in countries around the world. Therefore, precise estimates of its current and future trends are highly required for future policy implications.
Methods: We retrieved data from the Health Commission of Hubei, China. Logistic-S curve model was used to estimate the current and future trends of SARS-CoV-2-infected cases among 16 cities of Hubei, China from Jan-11 to Feb-24, 2020.
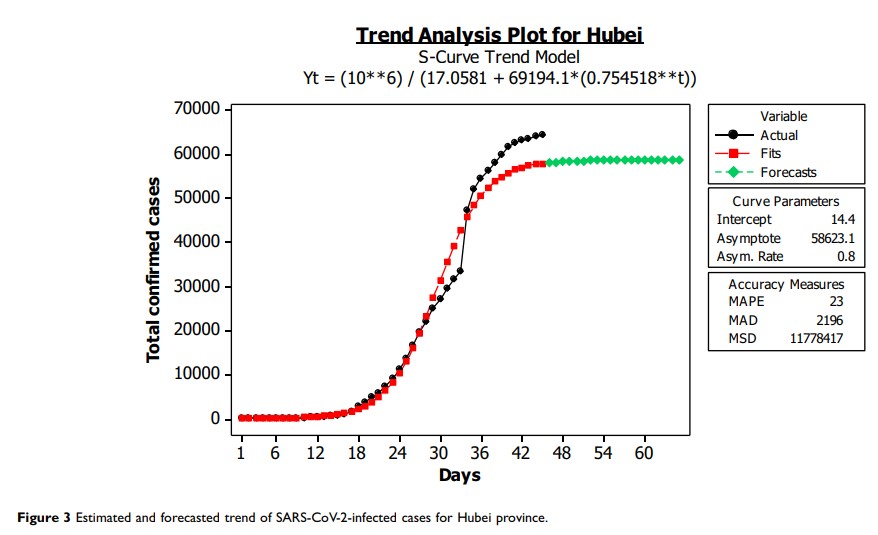
Results: Out of 64,287 confirmed cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Hubei, higher percentage of cases were in Wuhan and Xiaogan. The highest death percentage was found in Wuhan and Qianjiang. A significant percentage of cures were found in Enshi Prefecture and Huanggang, while Wuhan showed the lowest percentage of cures. Rising trends in infected cases were observed throughout the study period, particularly in Wuhan, and a higher trend was observed after 12-Feb. Gradual decline trend of SARS-CoV-2 cases was observed during Feb-25 to Mar-15 in Hubei Province. Future forecast showed that the average number of SARS-CoV-2-infected cases might be decreased or stable in Hubei in the coming 20 days.
Conclusion: The public must take precautionary measures in order to control and prevent disease spread and avoid extra travelling.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, death, trends, cities, Wuhan, China