110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肝移植术后出现术后谵妄的危险因素分析
Authors Chen J, Wang H, He Z, Li T
Received 21 March 2020
Accepted for publication 17 June 2020
Published 3 July 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 1645—1652
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S254920
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yu-Ping Ning
Purpose: The study aimed to analyze the incidence of postoperative delirium (POD) and associated risk factors after liver transplantation (LT).
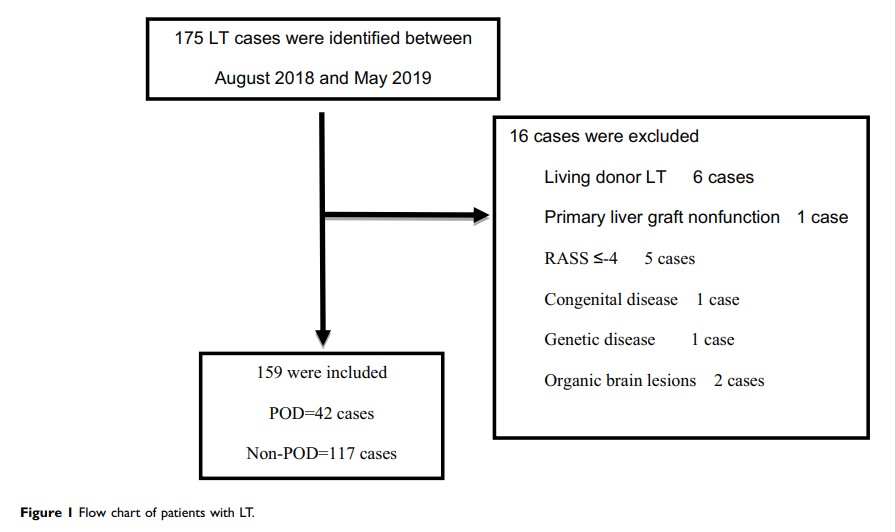
Patients and Methods: We identified and enrolled patients undergoing LT at the Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University between August 2018 and May 2019. We abstracted their relevant clinical information and assigned the patients into a POD group and non-POD group to compare differences in clinical information. Risk factors of POD were analyzed using logistic regression.
Results: A total of 159 LT patients were enrolled. Forty-two patients exhibited delirium (26.4%). Of the 42 with delirium, 33 (78.6%) had delirium within 3 days postoperatively and a median duration of 5 days (quartile 3– 7 days). The results of binary logistic regression are as follows: preoperative ammonia (≥ 46 vs < 46 μmol/L; OR 3.51, 95% CI [1.31– 9.46], P< 0.05), Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score (≥ 15 vs.< 15; OR 3.33, 95% CI [1.27– 8.79], P< 0.05), presence of hepatic encephalopathy (OR 3.30, 95% CI [1.20– 9.07], P< 0.05), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) on day 1 postoperatively (OR 1.33, 95% CI [1.06 − 1.68], P< 0.05), anhepatic period (OR 1.04, 95% CI [1.02 − 1.06], P< 0.01). The POD group had a longer intubation time (2925.0 vs 1410.0 min, P< 0.01), ICU length of stay (6 vs 4 d, P< 0.01) and increased medical costs (43.96 vs 33.74 ten thousand yuan, P< 0.01).
Conclusion: The incidence of POD in LT patients is a significant clinical feature. Ammonia ≥ 46 μmol/l, MELD score ≥ 15, hepatic encephalopathy, anhepatic period, and AST at 1 day postoperatively were independent risk factors for POD.
Keywords: liver transplantation, postoperative delirium, ammonia, hepatic encephalopathy, risk factors