110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

肿瘤和免疫细胞中 PD-L1 表达对食管鳞状细胞癌预后的交互作用:一项单中心回顾性队列研究
Authors Shi F, Xiao S, Miller KB, Zhao Y, Li Y, Gao Y, Chang H, Song Q, Qu C
Received 15 April 2020
Accepted for publication 1 June 2020
Published 3 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 6565—6572
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S258332
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Takuya Aoki
Purpose: The present study aimed to investigate the prognostic effect of PD-L1 expressing in tumor and immune cells among patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Patients and Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study by consecutively recruiting 142 patients. The clinicopathological features and PD-L1 expression on tumor and immune cells were independently evaluated by two pathologists.
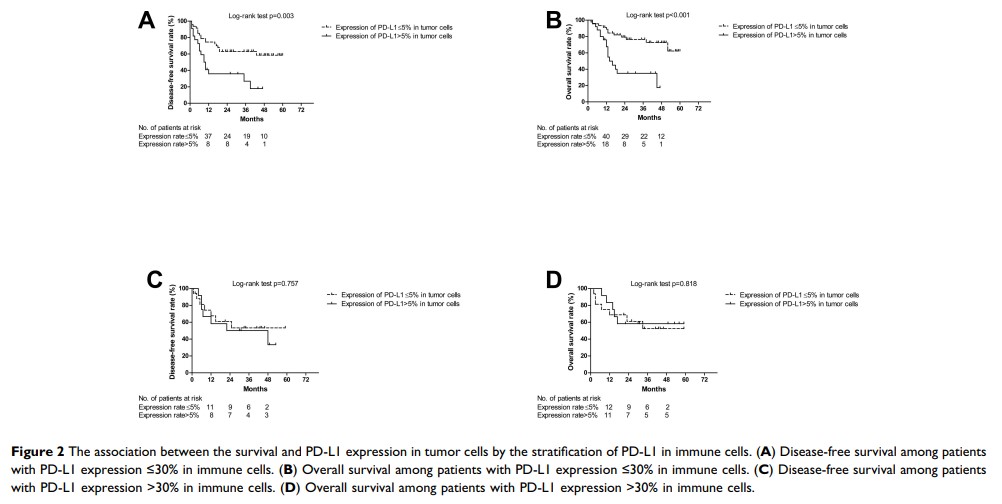
Results: The median expression rate of PD-L1 was 5% and 30% in tumor and immune cells, respectively. Patients with higher expression of PD-L1 in tumor cells had shorter disease-free and overall survival, and the HRs were 1.52 for relapse (95% CI: 0.88, 2.60) and 1.48 for death (95% CI: 0.82, 2.69). There was no significant association between the PD-L1 expression in immune cells and survival. However, among the patients with PD-L1 expression rate ≤ 30% in immune cells, the high expression rate of PD-L1 in tumor cells was significantly associated with the relapse and death, with HRs of 2.51 (95% CI: 1.25, 5.06) and 3.51 (95% CI: 1.57, 7.85), respectively. Among patients with PD-L1 expression rate > 30% in immune cells, the PD-L1 expression in tumor cells did not show any association with the disease-free and overall survival.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that the integration of PD-L1 expression in tumor and immune cells could be used to predict the relapse and survival among patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, PD-L1, prognosis, tumor cells and immune cells, tumor microenvironment