110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PD-1 和 PD-L1 在肿瘤浸润淋巴细胞中的表达可预测小细胞肺癌患者的预后
Authors Sun C, Zhang L, Zhang W, Liu Y, Chen B, Zhao S, Li W, Wang L, Ye L, Jia K, Wang H, Wu C, He Y, Zhou C
Received 1 March 2020
Accepted for publication 28 May 2020
Published 3 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 6475—6483
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S252031
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Takuya Aoki
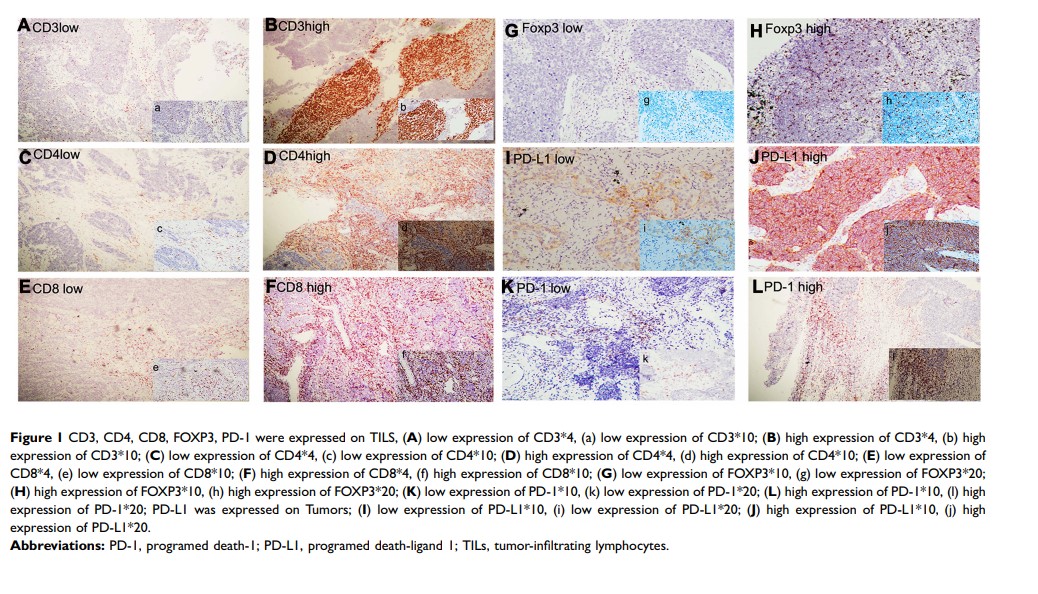
Introduction: Immune therapy has shown good results in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC), but the impact of immune microenvironment of the disease is unclear. In this work, we detected expression of programmed death 1 (PD-1), PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1), and other immune biomarkers of cancer. We also analyzed the correlations between these markers and survival in SCLC.
Patients and Methods: Protein expression of PD-1, PD-L1, PD-L2, CD3, CD4, CD8, and FOXP3 was analyzed in surgical tissues from 102 SCLC patients by immunohistochemistry.
Results: Positive expression of PD-1 on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) was found in 40.2% of patients; 37.3% of patients showed positive expression of PD-L1 on TILs; and 3.9% showed positive expression of PD-L1 on tumor cells. PD-L2 protein was not expressed on tumor cells or TILs. Survival analysis showed that positive expression of PD-L1 on TILs was correlated with longer relapse-free survival (RFS) (p=0.004). Positive expression of PD-1 combined with a high ratio of lymphocytes (CD3, p=0.004; CD4, p=0.011; CD8, p=0.009; FOXP3, p=0.009) was associated with significantly better RFS than negative expression of PD-1 combined with a lower ratio of lymphocytes. Positive expression of PD-L1 combined with a high ratio of lymphocytes (CD3, p< 0.001; CD4, p=0.001; CD8, p=0.002; FOXP3, p=0.001) was associated with significantly better RFS than negative expression of PD-L1 combined with a lower ratio of lymphocytes. All patients’ stage were between I and III.
Conclusion: PD-1 and PD-L1 expression might be good prognostic factors in SCLC.
Keywords: small-cell lung cancer, SCLC, programmed death-1, PD-1, programmed death-ligand 1, PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 2, PD-L2, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, TILs