110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MAP3K1 SNPs 和中国人群食管鳞状细胞癌易感性的危险因素之间的关联性研究:病例对照研究
Authors Yang Y, Zhou Q, Pan H, Wang L, Qian C
Received 8 April 2020
Accepted for publication 4 June 2020
Published 3 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 189—197
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PGPM.S256230
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Martin H Bluth
Purpose: The aim of this study was to screen the predisposed population and explore possible interactions between genetic polymorphisms and risk factors involved in the tumorigenesis and progression of ESCC (esophageal squamous cell carcinoma), in hope of identifying possible therapeutic targets along the way.
Patients and Methods: Cases (1043) and controls (1315) were enrolled to evaluate the possible association between MAP3K1 SNPs and ESCC risk. Subgroup analyses include MAP3K1 variants, gender, age, smoking and drinking status.
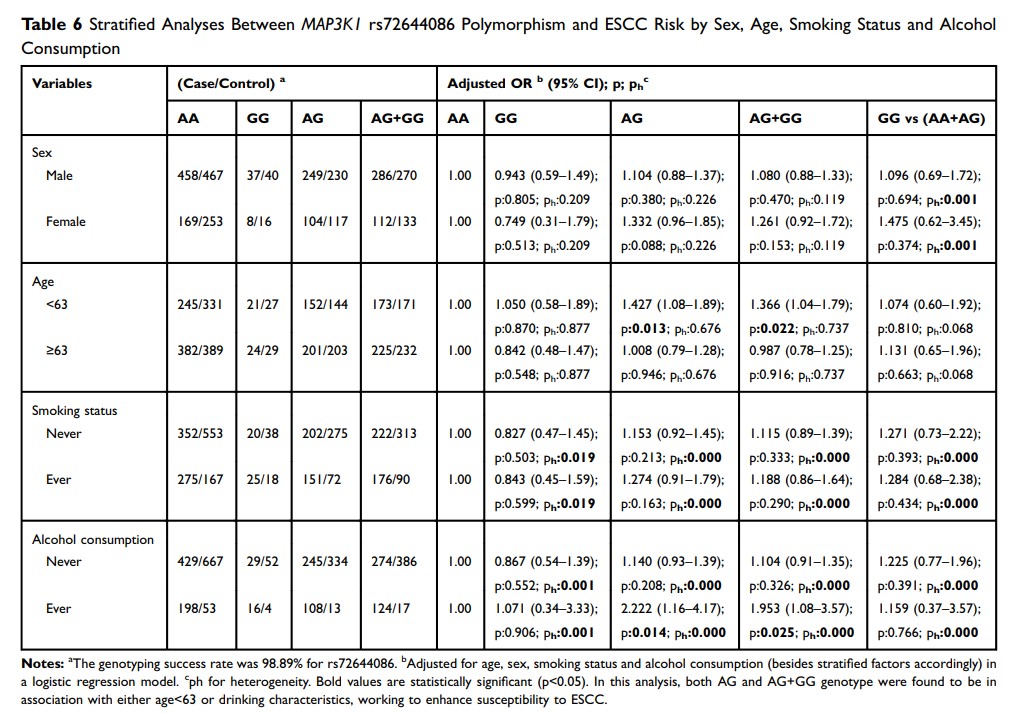
Results: Among all three single locus polymorphisms of MAP3K1 , only the heterozygote genotype of rs702689 AG is shown to be associated with increased risk for developing ESCC (OR=1.272, 95% confidence interval=1.061– 1.525, p=0.009). Moreover, stratified analysis results observed altered susceptibility among patients with exposure to risk factors combined with certain genetic variant to ESCC.
Conclusion: This study reveals that MAP3K1 rs702689 AG genotype might facilitate the tumorigenesis in ESCC, particularly among women, patients who were over 63y and those who never drink nor smoke.
Keywords: single nucleotide polymorphism, esophageal cancer