110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

阿帕替尼治疗不可切除的肝内胆管癌的疗效和安全性:一项观察性研究
Authors Hu Y, Lin H, Hao M, Zhou Y, Chen Q, Chen Z
Received 22 March 2020
Accepted for publication 11 June 2020
Published 3 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 5345—5351
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S254955
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yong Teng
Purpose: Unresectable intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) has a poor prognosis. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of apatinib for patients with unresectable ICC.
Patients and Methods: A total of 10 patients with unresectable ICC were enrolled for this single-center observational study between March 2, 2016, and August 27, 2019. Subjects received 500 mg apatinib on a daily basis. Tumor response was assessed by 1.1 response evaluation criteria in solid tumors. The progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were calculated using the Kaplan–Meier method. The drug-related adverse effects were also monitored.
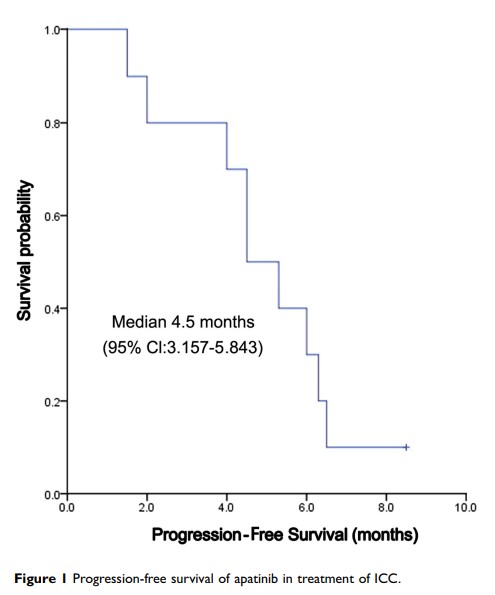
Results: Based on the follow-up computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging after treatment, 4 (40.0%), 4 (40.0%), and 2 (20.0%) patients achieved a partial response, stable disease, and progression of the disease, respectively. The response rate and disease control rate were 40.0% and 80.0%, respectively. The median PFS was 4.5 months (95% confidence interval: 3.157∼ 5.843 months); the median OS was 6.5 months (95% confidence interval: 4.744∼ 8.256 months). Furthermore, 3-, 6-, and 9-month OS rates were 77.5%, 61.7%, and 15.0%, respectively. The most common hematologic grade 3 adverse event was neutropenia (10%); the most common nonhematologic grade 3 adverse events were hypertension (20.0%) and hand-foot syndromes (20.0%). No treatment-related grade 4 or 5 adverse events were recorded.
Conclusion: Apatinib revealed to have antitumour activity in unresectable ICC patients, with manageable toxicities, and thus might be used as a new treatment option for patients with unresectable ICC.
Keywords: apatinib, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, targeted therapy, efficacy, safety