110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

IGFBP5 过表达通过 PI3K-AKT 信号通路增强前列腺癌的放射敏感性
Authors Chen X, Yu Q, Pan H, Li P, Wang X, Fu S
Received 10 April 2020
Accepted for publication 29 May 2020
Published 6 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 5409—5418
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S257701
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
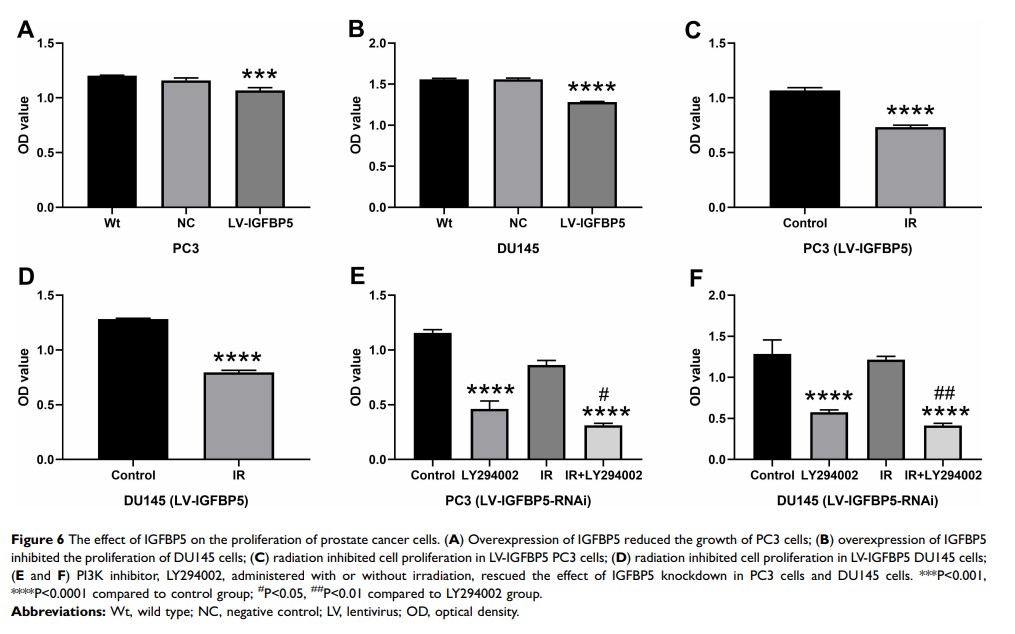
Background: Radiotherapy is the main treatment for localized prostate cancer. The therapeutic effects of radiotherapy are highly dependent on radiosensitivity of target tumors. Here, we investigated the impact of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) on irradiation therapy in prostate cancer.
Methods: IGFBP5 gene was overexpressed in human prostate cancer cell lines, PC3 and DU145, with transfection of lentivirus expression vector. Radiosensitivity of the cell lines was assessed with colony formation, cell cycle and cell proliferation assays. The expression of proteins associated with the PI3K-AKT pathway was determined by Western blotting. The effect of IGFBP5 knockdown on PI3K-AKT pathway was tested using PI3K inhibitor.
Results: Higher expression of IGFBP5 improved the efficacy of radiotherapy for prostate cancer patients. The effects of IGFBP5 were linked to the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Overexpression of IGFBP5 enhanced radiosensitivity and induced G2/M phase arrest in prostate cancer cells. In contrast, it decreased PI3K, p-AKT expression and cell viability. These effects were reversed by IGFBP5 knockdown.
Conclusion: Our results reveal that IGFBP5 regulates radiosensitivity in prostate cancer via the PI3K-AKT pathway. It is, therefore, a potential biomarker of tumors that influences the therapeutic effect of radiotherapy.
Keywords: IGFBP5, irradiation, prostate cancer, radiosensitivity, PI3K-AKT pathway