110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

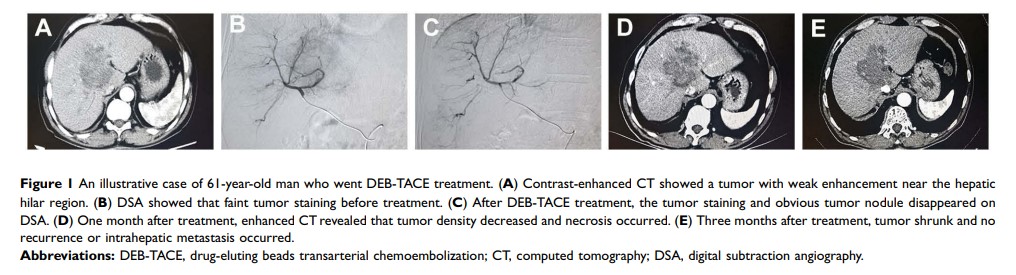
药物洗脱珠与脂质体经动脉化疗栓塞治疗用于少血供肝细胞癌治疗的对比:单中心回顾性研究
Authors Shi Q, Chen D, Zhou C, Liu J, Huang S, Yang C, Xiong B
Received 28 March 2020
Accepted for publication 28 May 2020
Published 6 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 5461—5468
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S255960
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yong Teng
Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of drug-eluting beads transarterial chemoembolization (DEB-TACE) and conventional TACE (C-TACE) in treating hypovascular hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Materials and Methods: The medical records based on HCC patients who underwent TACE from January 2016 to June 2019 were reviewed in the study. The diagnosis of hypovascular HCC was conducted by two senior radiologists according to imaging. We evaluated the adverse events (AEs), objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in the study.
Results: A total of 98 patients with hypovascular HCC were included in the study. 46 patients underwent DEB-TACE treatment, and 52 patients underwent C-TACE treatment. The PFS of DEB-TACE group and C-TACE group was 12.0 months and 7.0 months (P < 0.001), and OS was 21.0 months and 14.0 months (P = 0.035), respectively. In addition, DEB-TACE group had better ORR (76.1% vs 40.4%, P < 0.001) and DCR (91.3% vs 75.0%, P = 0.033) compared to C-TACE group. The occurrence rate of AEs showed no difference between the two groups (67.3% vs 57.7%, P = 0.323). Furthermore, we found that DEB-TACE can be identified as a positive independent prognostic factor for improved PFS and OS.
Conclusion: DEB-TACE, as an effective treatment, can yield better objective response rate, similar safety profile and improved survival for hypovascular HCC patients compared to C-TACE.
Keywords: hypovascular hepatocellular carcinoma, drug-eluting beads, lipiodol, transarterial chemoembolization, survival