110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在腰背部相关的腿痛中主要体觉皮质区的超连通性和高时空变异性:静态和动态功能连通性的 fMRI 研究
Authors Pei Y, Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Zhao Y, Zhou F, Huang M, Wu L, Gong H
Received 18 December 2019
Accepted for publication 23 May 2020
Published 6 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1665—1675
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S242807
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael A Überall
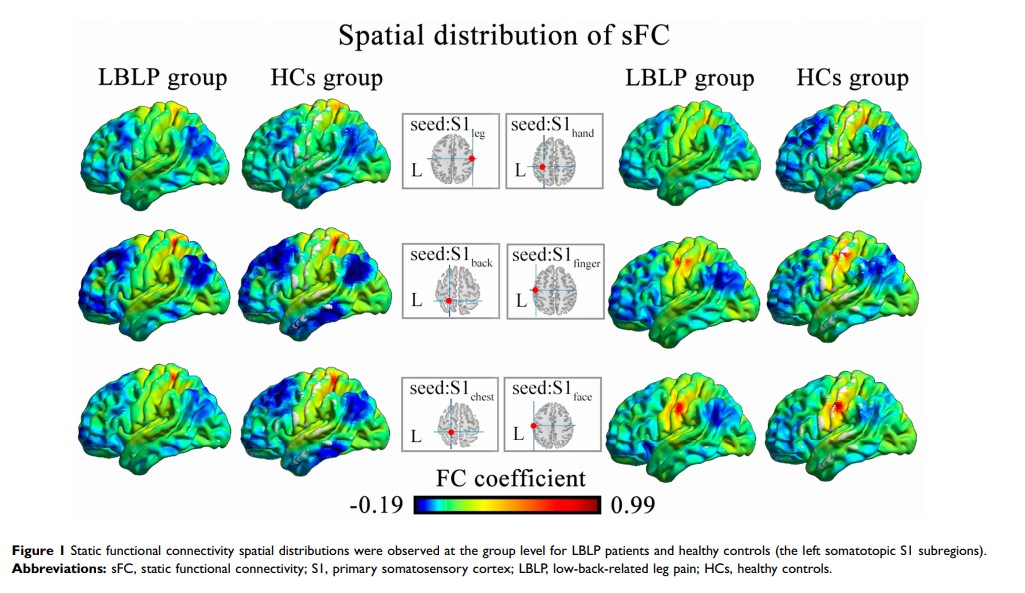
Objective: To investigate the functional connectivity (FC) and its variability in the primary somatosensory cortex (S1) of patients with low-back-related leg pain (LBLP) in the context of the persistent stimuli of pain and numbness.
Patients and Methods: We performed functional magnetic resonance imaging on LBLP patients (n = 26) and healthy controls (HCs; n = 34) at rest. We quantified and compared static FC (sFC) using a seed-based analysis strategy, with 6 predefined bilateral paired spherical regions of interest (ROIs) in the S1 cortex. Then, we captured the dynamic FC using sliding window correlation of ROIs in both the LBLP patients and HCs. Furthermore, we performed a correlational analysis between altered static and dynamic FC and clinical measures in LBLP patients.
Results: Compared with controls, the LBLP patients had 1) significantly increased static FC between the left S1back (the representation of the back in the S1) and right superior and middle frontal gyrus (SFG/MFG), between the left S1chest and right SFG/MFG, between right S1chest and right SFG/MFG, between the left S1face and right MFG, and between the right S1face and right inferior parietal lobule (P < 0.001, Gaussian random field theory correction); 2) increased dynamic FC only between the right S1finger and the left precentral and postcentral gyrus and between the right S1hand and the right precentral and postcentral gyrus (P < 0.01, Gaussian random field theory correction); and 3) a negative correlation between the Barthel index and the increased static FC between the left S1face and right inferior parietal lobule (P = 0.048).
Conclusion: The present study demonstrated the hyperconnectivity of the S1 cortex to the default mode and executive control network in a spatial pattern and an increase in the tendency for signal variability in the internal network connections of the S1 cortex in patients with LBLP.
Keywords: primary somatosensory cortex, static functional connectivity, dynamic functional connectivity, chronic low-back-related leg pain, chronic pain, resting-state functional MRI