110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

超声与核心交联纳米系统相结合,可增强阿霉素前体药物/β-拉帕酮在肿瘤中的渗透
Authors Li Q, Hou W, Li M, Ye H, Li H, Wang Z
Received 25 February 2020
Accepted for publication 10 June 2020
Published 7 July 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 4825—4845
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S251277
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
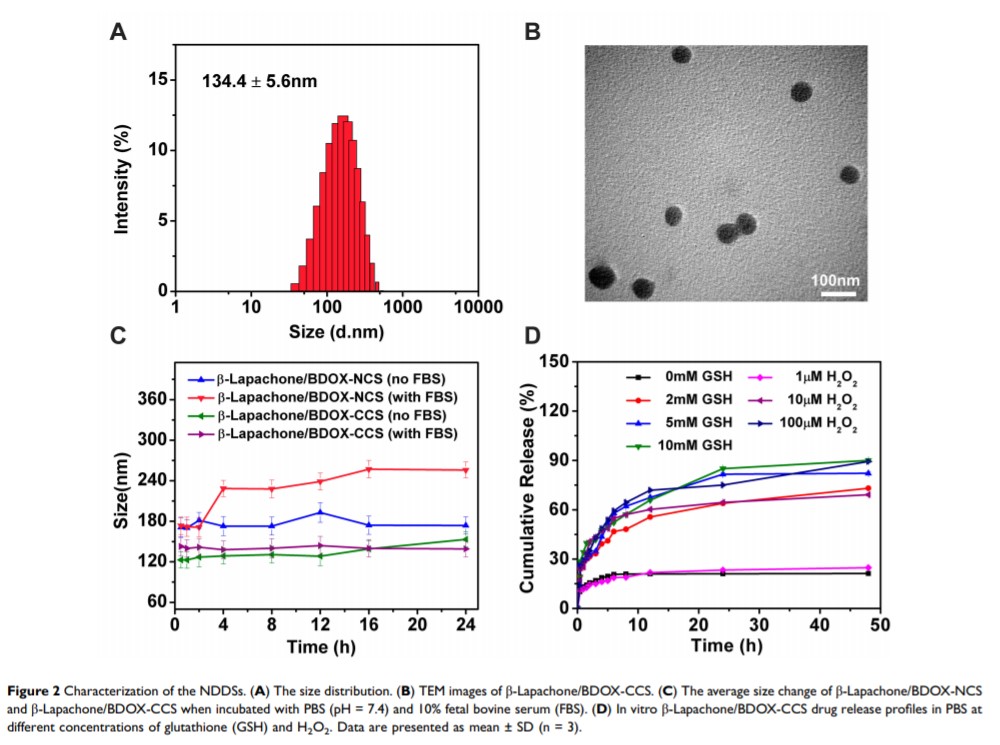
Background: Nanosized drug delivery systems (NDDSs) have shown excellent prospects in tumor therapy. However, insufficient penetration of NDDSs has significantly impeded their development due to physiological instability and low passive penetration efficiency.
Methods: Herein, we prepared a core cross-linked pullulan-modified nanosized system, fabricated by visible-light-induced diselenide bond cross-linked method for transporting β-Lapachone and doxorubicin prodrug (boronate-DOX, BDOX), to improve the physiological stability of the NDDSs for efficient passive accumulation in tumor blood vessels (β-Lapachone/BDOX-CCS). Additionally, ultrasound (US) was utilized to transfer β-Lapachone/BDOX-CCS around the tumor vessel in a relay style to penetrate the tumor interstitium. Subsequently, β-Lapachone enhanced ROS levels by overexpressing NQO1, resulting in the transformation of BDOX into DOX. DOX, together with abundant levels of ROS, achieved synergistic tumor therapy.
Results: In vivo experiments demonstrated that ultrasound (US) + cross-linked nanosized drug delivery systems (β-Lapachone/BDOX-CCS) group showed ten times higher DOX accumulation in the tumor interstitium than the non-cross-linked (β-Lapachone/BDOX-NCS) group.
Conclusion: Thus, this strategy could be a promising method to achieve deep penetration of NDDSs into the tumor.
Keywords: nanosized drug delivery system, core cross-linked, physiological stability, ultrasound, deep tumor penetration