110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

大肠癌 N2 表型中性粒细胞中的 miRNA 表达谱与假定的关键 miRNA 的筛选
Authors Wang L, Yang J, Huang J, Wen ZQ, Xu N, Liu X, Zhang JH, Li WL
Received 26 February 2020
Accepted for publication 26 May 2020
Published 7 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 5491—5503
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S251427
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Objective: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in the digestive tract, which accounts for 10% of all the malignant tumors in the world. The aim of this study was to identify key genes and miRNAs in CRC diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy and to further explore the potential molecular mechanisms of CRC.
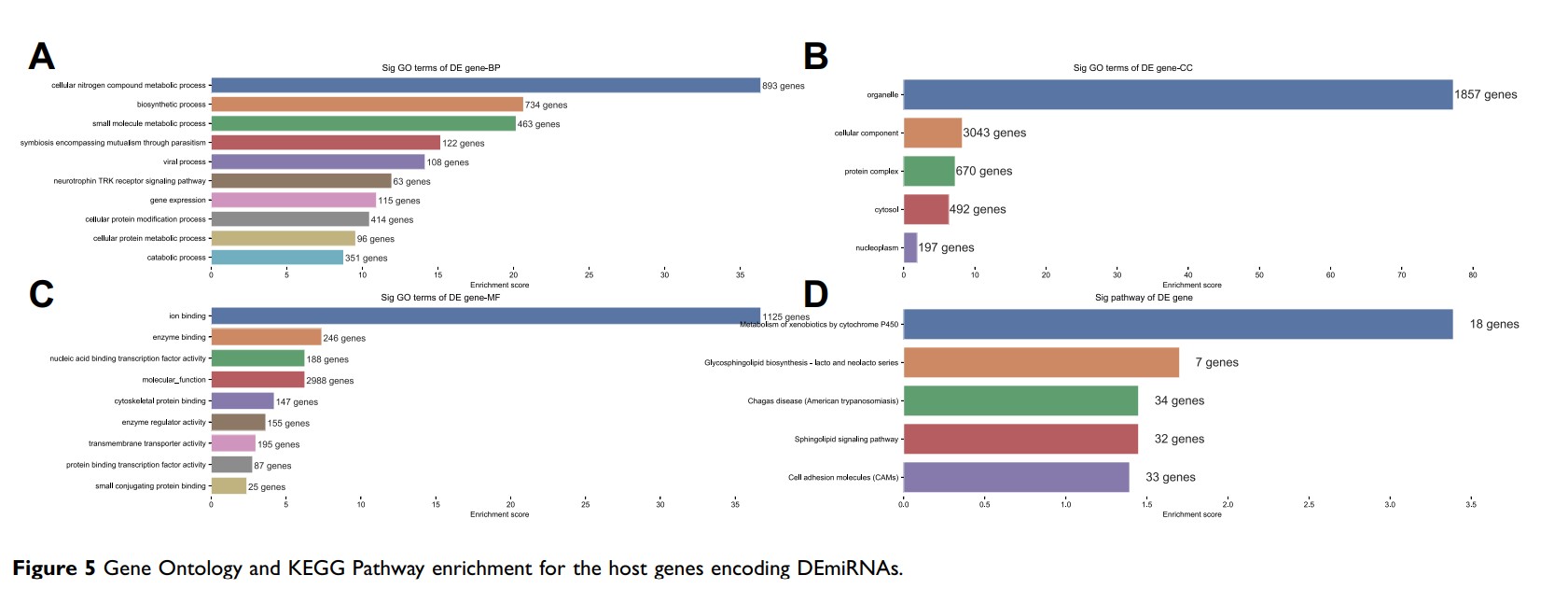
Methods: The infiltration and metastasis of neutrophils in primary colorectal cancer tissue and paracancerous tissue were observed by immunohistochemical staining. After inducing N2 neutrophils with TGF-β 1 in vitro, exosomes were extracted and sequenced, and then the expression differences of miRNAs were screened by using Agilent miRNA microarrays. The data were imported to the Web CARMA for differential expression analysis. The GO and KEGG enrichment analysis were performed using DIANA-MirPath v3.0 using TargetScan database. And the corresponding targets were imported into Gephi for network analysis. The expression level of differentially expressed miRNA using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was validated.
Results: A total of 2 miRNAs were found to be associated with N2 neutrophils, in which the expression of hsa-miR-4780 was upregulated and the expression of hsa-miR-3938 was downregulated in N2 neutrophils, compared with the neutrophils. In addition, the results of miRNA-targets networks showed that the hsa-mir-3938 and hsa-mir-4780 could regulate TUSC1 and ZNF197. The expression level of hsa-miR-4780 and hsa-miR-3938 wase validated in accordance with the results of RT-PCR.
Conclusion: The hsa-mir-3938 and hsa-mir-4780 were differentially expressed between N2 neutrophils and neutrophils. Moreover, the regulation of TUSC1 and ZNF197 by these DEmiRNA established the theoretical basis for the mechanism of N2 type neutrophils regulating the invasion and metastasis of CRC cells and provided the potential biomarker for prognosis for clinical treatment of CRC.
Keywords: miRNA, N2 phenotype neutrophils, colorectal cancer