110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

晚期非小细胞肺癌对安罗替尼的治疗反应与 TP53 突变之间的关联
Authors Fang S, Cheng W, Zhang M, Yang R
Received 9 April 2020
Accepted for publication 15 June 2020
Published 7 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 6645—6650
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S257052
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
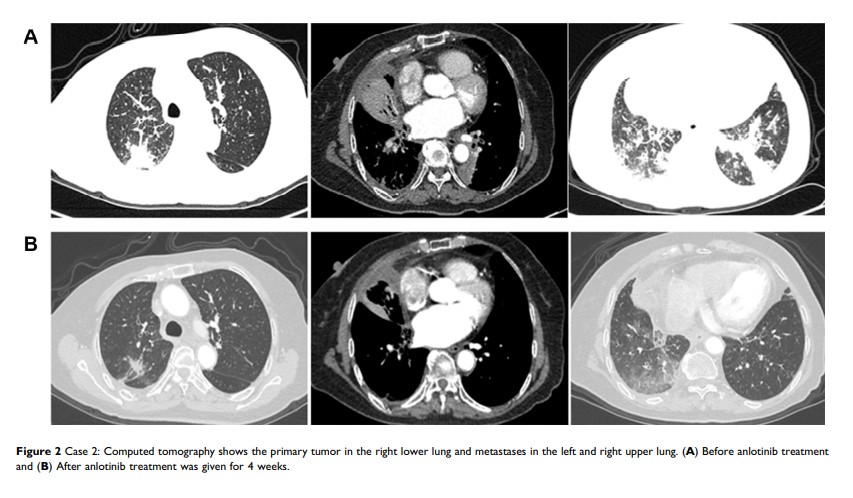
Abstract: Multitargeted antiangiogenic drugs have demonstrated significant antitumor activity against a variety of solid tumors. Anlotinib, a novel oral multitargeted antiangiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitor, was approved as a third-line treatment for advanced NSCLC in China. However, predictive biomarkers are currently insufficient and are urgently required. Herein, we report three pre-treated cases of advanced NSCLC with TP53 mutations, wherein these patients showed partial response to anlotinib. Moreover, the three patients have achieved a progression-free survival of 8, 6.5, and 5 months, respectively. The main toxicities were hypertension, hand-foot syndrome and fatigue. In conclusion, TP53 mutations may represent a biomarker for predicting salutary effects of anlotinib.
Keywords: non-small cell lung cancer, angiogenesis, anlotinib, TP53