110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

腰大肌区域指数对评估肌肉减少症、肌肉减少症超重/肥胖症很有价值,并可预测接受开腹胰十二指肠切除术患者的预后
Authors Xu JY, Li C, Zhang H, Liu Y, Wei JM
Received 10 April 2020
Accepted for publication 26 June 2020
Published 9 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 761—770
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S257677
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Marco Carotenuto
Background and Aim: Sarcopenia has been proven to be a risk factor after pancreatoduodenectomy (PD). We aimed to evaluate if decreased psoas muscle area and density shown in CT scan, as measures for sarcopenia, were associated with postoperative major complications and adverse outcomes in patients who underwent PD.
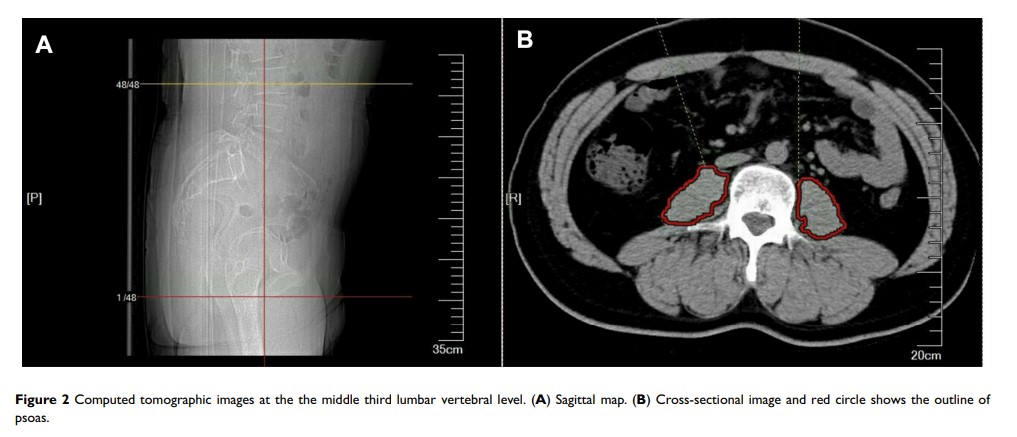
Patients and Methods: We analyzed 152 consecutive patients who underwent open PD. Total psoas area and muscle attenuation were measured on CT images at the level of the third lumbar vertebra. Total psoas area index (TPAI) was calculated, the cut-off values of TPAI were estimated and validated. The relationship between radiographic characters and outcomes was analyzed.
Results: The optimal cut-off values of TPAI were 4.78 cm2/m2 for males and 3.46 cm2/m2 for females. The values were validated by outcomes with significant differences in the rate of major complications, re-operation, length of stay, and total cost. The prevalence of TPAI-defined sarcopenia and sarcopenic overweight/obesity was 38.8% and 17.1% in total. In multivariate logistic regression, rate of major complications was associated with TPAI [OR=0.605, 95% CI (0.414, 0.883), P =0.009], TPAI-defined sarcopenia [OR=8.256, 95% CI (2.890, 23.583), P =0.000] and sarcopenic overweight/obesity [OR=7.462, 95% CI (2.084, 26.724), P =0.002]; meanwhile, NRS2002-defined nutritional risk and GLIM-defined malnutrition did not show relationship with major complications.
Conclusion: Both sarcopenia and sarcopenic overweight/obesity determined by new TPAI cut-off values were associated with a higher rate of major complications and adverse outcomes in Chinese patients undergoing open PD whereas usual nutritional assessment was not.
Keywords: psoas muscle area index, CT scan, sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity, pancreatoduodenectomy