110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长链基因间非蛋白质编码 RNA 1089 通过调节 miRNA-27a-3p/上皮-间质转化(EMT)轴来抑制胃癌细胞的增殖和转移
Authors Yang F, Chen X, Li X, Chen J, Tang Y, Cai Y, Wang Y, Chen Z, Li L, Li R, Deng Z
Received 18 March 2020
Accepted for publication 11 June 2020
Published 9 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 5587—5596
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S254064
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
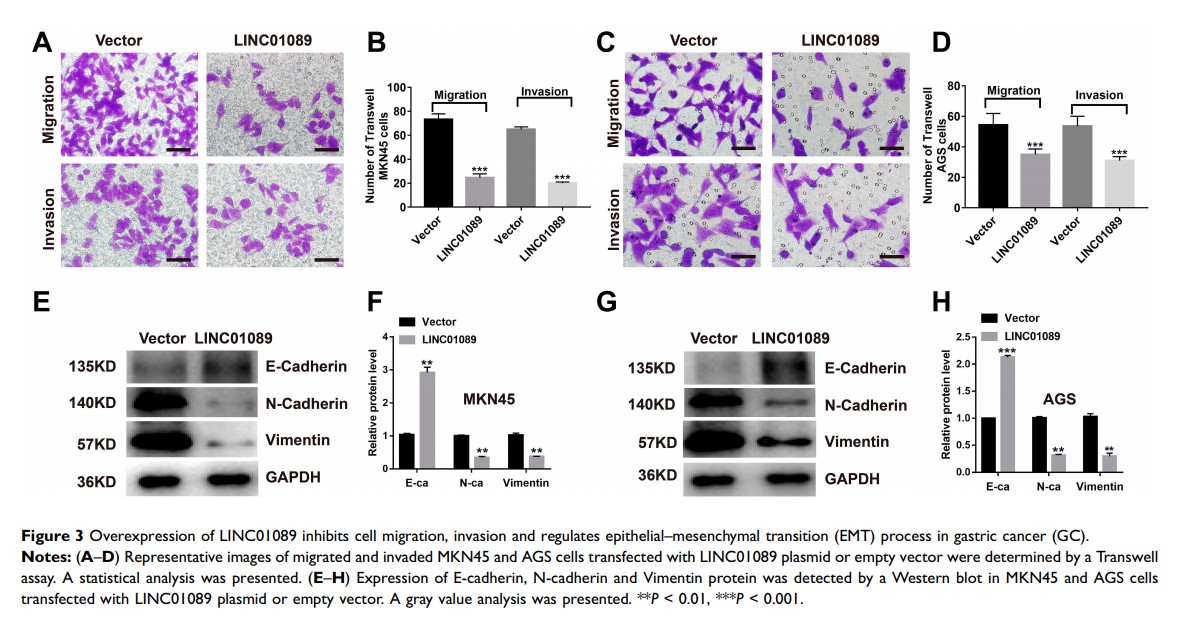
Aim: To explore the expression and biological function of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1089 (LINC01089) in gastric cancer (GC) progression and its underlying mechanism.
Methods: LINC01089 and microRNA-27a-3p (miR-27a-3p) expressions were detected with the quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Cell proliferation, migration and invasion were evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and Transwell assay. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related proteins were also measured by Western blot. The relationship between LINC01089 and miR-27a-3p was revealed by a bioinformatics analysis and dual-luciferase reporter assay.
Results: LINC01089 was significantly down-regulated in GC tissues, as well as GC cell lines. GC patients with lower LINC01089 expression were more likely to have poor outcomes. Overexpression of LINC01089 significantly suppressed GC cells growth, migration and invasion and forbade the EMT process. LINC01089 was directly targeted at miR-27a-3p. The transfection of miR-27a-3p mimics reversed the inhibitory effects on proliferative and metastatic abilities of GC cells with LINC01089 overexpression.
Conclusion: LINC01089 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in GC by targeting miR-27a-3p/EMT axis, which should be considered as a promising therapeutic target.
Keywords: LINC01089, miRNA-27a-3p, proliferation, metastasis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), gastric cancer (GC)