110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

甲基转移酶 NSD2 在人实体瘤中的潜在致癌基因作用
Authors Chen R, Chen Y, Zhao W, Fang C, Zhou W, Yang X, Ji M
Received 25 April 2020
Accepted for publication 10 June 2020
Published 13 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 6837—6846
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S259873
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
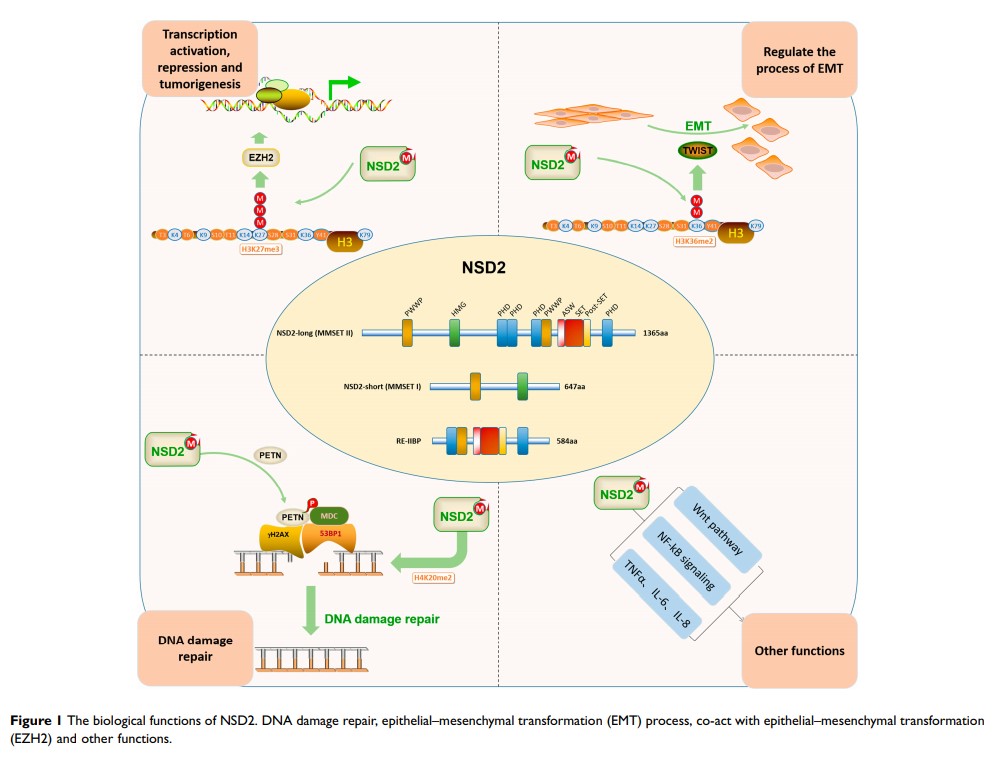
Abstract: Malignant solid tumors are the leading cause of death in humans, and epigenetic regulation plays a significant role in studying the mechanism of human solid tumors. Recently, histone lysine methylation has been demonstrated to be involved in the development of human solid tumors due to its epigenetic stability and some other advantages. The 90-kb protein methyltransferase nuclear receptor SET domain-containing 2 (NSD2) is a member of nuclear receptor SET domain-containing (NSD) protein lysine methyltransferase (KMT) family, which can cause epigenomic aberrations via altering the methylation states. Studies have shown that NSD2 is frequently over-expressed in multiple types of aggressive solid tumors, including breast cancer, renal cancer, prostate cancer, cervical cancer, and osteosarcoma, and such up-regulation has been linked to poor prognosis and recurrence. Further studies have identified that over-expression of NSD2 promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transformation (EMT), suggesting its potential oncogenic role in solid tumors. Moreover, Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) was searched for validation of prognostic value of NSD2 in human solid tumors. However, the underlying specific mechanism remains unclear. In our present work, we summarized the latest advances in NSD2 expression and clinical applications in solid tumors, and our findings provided valuable insights into the targeted therapeutic regimens of solid tumors.
Keywords: NSD2, proliferation, migration, invasion, EMT, oncogene