108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

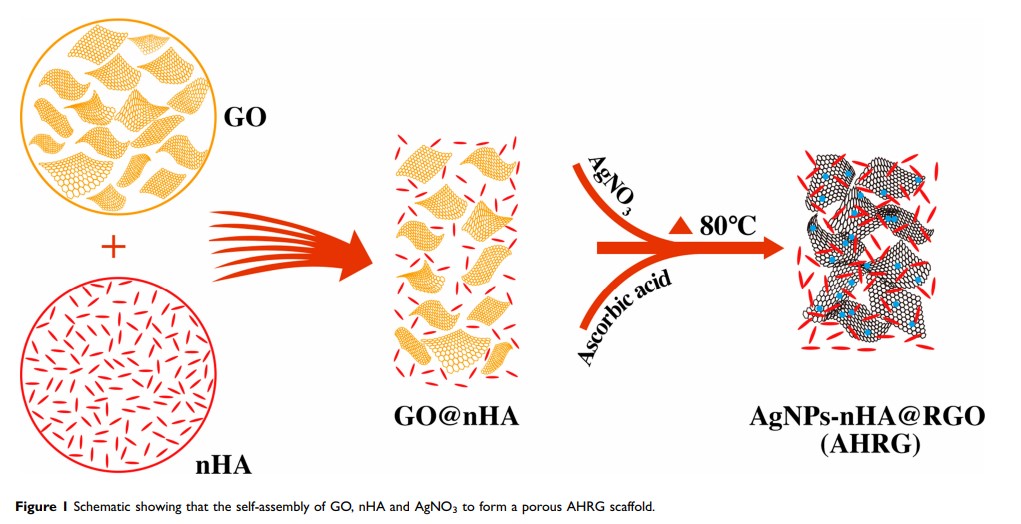
AgNP-nHA@RGO 三维多孔支架的一步制备及其在感染性骨缺损治疗中的应用
Authors Weng W, Li X, Nie W, Liu H, Liu S, Huang J, Zhou Q, He J, Su J, Dong Z, Wang D
Received 11 December 2019
Accepted for publication 25 May 2020
Published 14 July 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 5027—5042
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S241859
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Background: Bactericidal capacity, durable inhibition of biofilm formation, and a three-dimensional (3D) porous structure are the emphases of infected bone defect (IBD) treatment via local scaffold implantation strategy.
Purpose: In this study, silver nanoparticle (AgNP)-loaded nano-hydroxyapatite (nHA)@ reduced graphene oxide (RGO) 3D scaffolds (AHRG scaffolds) were designed to alleviate bone infection, inhibit biofilm formation, and promote bone repair through the synergistic effects of AgNPs, RGO, and nHA.
Materials and Methods: AHRGs were prepared using a one-step preparation method, to create a 3D porous scaffold to facilitate a uniform distribution of AgNPs and nHA. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was used as a model-resistant bacterium, and the effects of different silver loadings on the antimicrobial activity and cytocompatibility of materials were evaluated. Finally, a rabbit IBD model was used to evaluate the therapeutic effect of the AHRG scaffold in vivo.
Results: The results showed successful synthesis of the AHRG scaffold. The ideal 3D porous structure was verified using scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and selected area electron diffraction measurements revealed uniform distributions of AgNP and nHA. In vitro antibacterial and cytocompatibility indicated that the 4% AHRG scaffolds possessed the most favorable balance of bactericidal properties and cytocompatibility. In vivo evaluation of the IBD model showed promising treatment efficacy of AHRG scaffolds.
Conclusion: The as-fabricated AHRG scaffolds effectively eliminated infection and inhibited biofilm formation. IBD repair was facilitated by the bactericidal properties and 3D porous structure of the AHRG scaffold, suggesting its potential in the treatment of IBDs.
Keywords: biofilm, graphene oxide, hydroxyapatite, infected bone defect, scaffold, silver nanoparticles, three-dimensional