108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

丹诺普韦用于治疗丙型肝炎病毒感染:设计、开发及在治疗中的应用
Authors Miao M, Jing X, De Clercq E, Li G
Received 25 March 2020
Accepted for publication 12 June 2020
Published 14 July 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2759—2774
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S254754
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
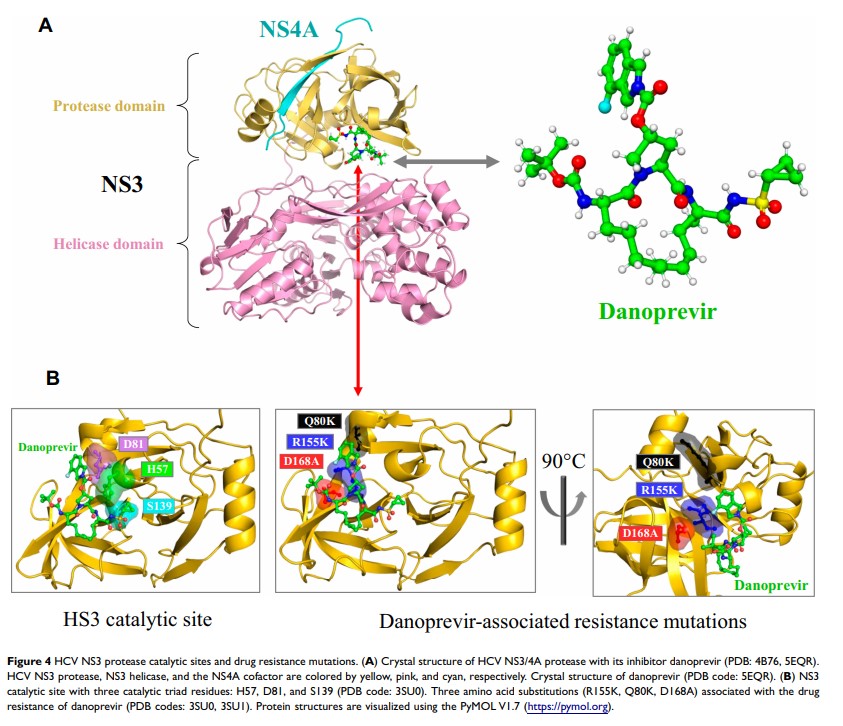
Abstract: On June 8, 2018, an NS3/4A protease inhibitor called danoprevir was approved in China to treat the infections of HCV genotype (GT) 1b – the most common HCV genotype worldwide. Based on phase 2 and 3 clinical trials, the 12-week regimen of ritonavir-boosted danoprevir (danoprevir/r) plus peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin offered 97.1% (200/206) of sustained virologic response at post-treatment week 12 (SVR12) in treatment-naïve non-cirrhotic patients infected with HCV genotype 1b. Adverse events such as anemia, fatigue, fever, and headache were associated with the inclusion of peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin in the danoprevir-based regimen. Moreover, drug resistance to danoprevir could be traced to amino acid substitutions (Q80K/R, R155K, D168A/E/H/N/T/V) near the drug-binding pocket of HCV NS3 protease. Despite its approval, the clinical use of danoprevir is currently limited to its combination with peginterferon alpha-2a and ribavirin, thereby driving its development towards interferon-free, ribavirin-free regimens with improved tolerability and adherence. In the foreseeable future, pan-genotypic direct-acting antivirals with better clinical efficacy and less adverse events will be available to treat HCV infections worldwide.
Keywords: danoprevir, ITMN-191, R7227, HCV NS3/4A inhibitor, HCV genotype