108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

丹参酮 IIA 通过抑制 Nogo-A/NgR1/RhoA/ROCKII/MLC 信号传导促进局灶性脑缺血大鼠的轴突再生
Authors Wang J, Ni G, Liu Y, Han Y, Jia L, Wang Y
Received 10 March 2020
Accepted for publication 12 June 2020
Published 15 July 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2775—2787
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S253280
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Manfred Ogris
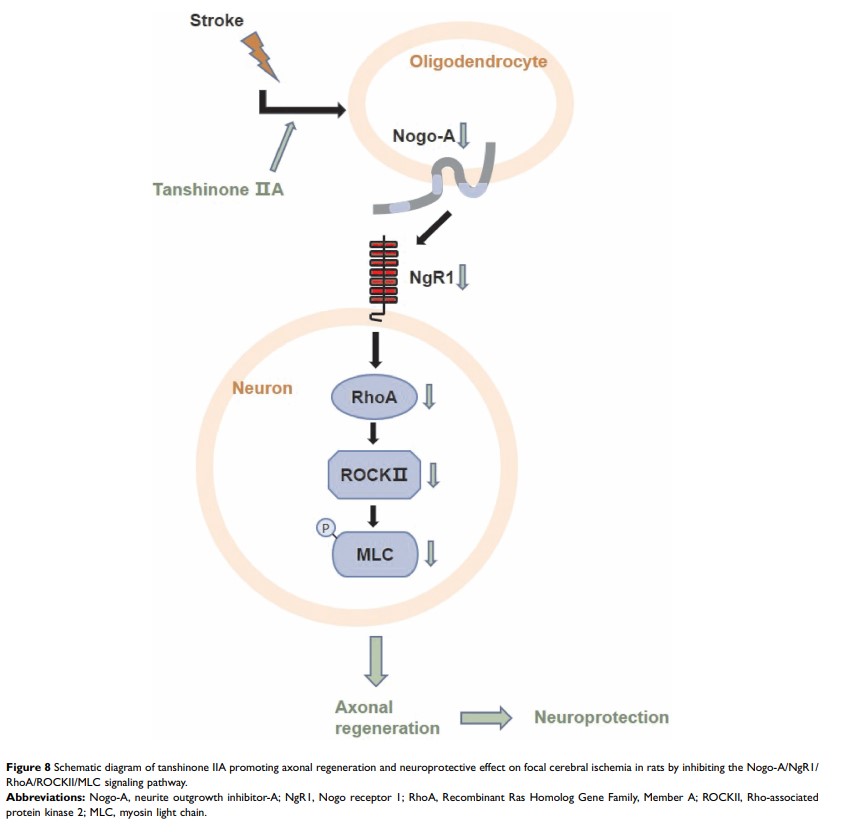
Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate the neuroprotective effect of tanshinone IIA (TSA) on focal cerebral ischemia in rats and to investigate whether it was associated with Nogo-A/NgR1/RhoA/Rho-associated protein kinase 2 (ROCKII)/myosin light chain (MLC) signaling.
Methods: In this study, focal cerebral ischemia animal model was used. Neurological deficit scores and infarction volume were investigated to evaluate the neuroprotection of TSA. Hematoxylin-eosin staining, Nissl staining, and immunofluorescence staining were conducted to detect ischemic changes in brain tissue and changes in neurofilament protein 200 (NF200) and growth-associated protein-43 (GAP-43) expression, respectively. Western blotting and qRT-PCR analyses were used to detect the expression levels of NF200, GAP-43 and Nogo-A/NgR1/RhoA/ROCKII/MLC pathway-related signaling molecules.
Results: TSA treatment can improve the survival rate of rats, reduce the neurological score and infarct volume, and reduce neuron damage. In addition, TSA also increased axon length and enhanced expression of NF200 and GAP-43. Importantly, TSA significantly attenuated the expression of Nogo-A, NgR1, RhoA, ROCKII, and p-MLC, and thus inhibiting the activation of this signaling pathway.
Conclusion: TSA promoted axonal regeneration by inhibiting the Nogo-A/NgR1/RhoA/ROCKII/MLC signaling pathway, thereby exerting neuroprotective effects in cerebral ischemia rats, which provided support for the clinical application of TSA in stroke treatment.
Keywords: tanshinone IIA, cerebral ischemia, axonal regeneration, neuroprotective effect, neurite outgrowth inhibitor-A, Nogo receptor, Rho-associated protein kinase