108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

丹皮酚通过调节 miR-21-5p/KLF6 轴抑制肝癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并诱导细胞凋亡
Authors Cai M, Shao W, Yu H, Hong Y, Shi L
Received 18 March 2020
Accepted for publication 24 June 2020
Published 17 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 5931—5943
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S254485
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common tumors with high mortality. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) were reported as crucial markers for the diagnosis of HCC. Paeonol exerted many pharmacological effects on tumor progression. This study aimed to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanism of paeonol in HCC progression.
Methods: Cell viability was determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Cell apoptosis was examined by flow cytometry. The levels of Cyclin D1, cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) and Bcl-2 associated X protein (Bax) were detected by Western blot assay. Cell migration and invasion were assessed by transwell assay. The levels of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9) were measured by Western blot. The expression of miR-21-5p and kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6) was detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) or Western blot assay, respectively. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to analyze the interaction between miR-21-5p and KLF6. The enrichment of miR-21-5p was determined by RNA pull-down assay. Xenograft assay was conducted to analyze tumor growth in vivo.
Results: The results demonstrated that cell viability of Hep3B and Huh-7 cells was inhibited, while cell apoptosis was promoted after treatment with paeonol. Transwell assay indicated that cell migration and invasion were blocked in paeonol-treated cells. Moreover, miR-21-5p expression was markedly decreased in paeonol-treated cells and its knockdown suppressed cell viability, migration and invasion, but contributed to cell apoptosis. MiR-21-5p targeted KLF6 and its silencing prominently elevated KLF6 level. Furthermore, the restoration experiment determined that miR-21-5p and KLF6 were antagonisms on cell viability, apoptosis, migration and invasion. Also, paeonol abated the decrease in KLF6 level caused by miR-21-5p up-regulation. Besides, paeonol suppressed tumor growth in vivo.
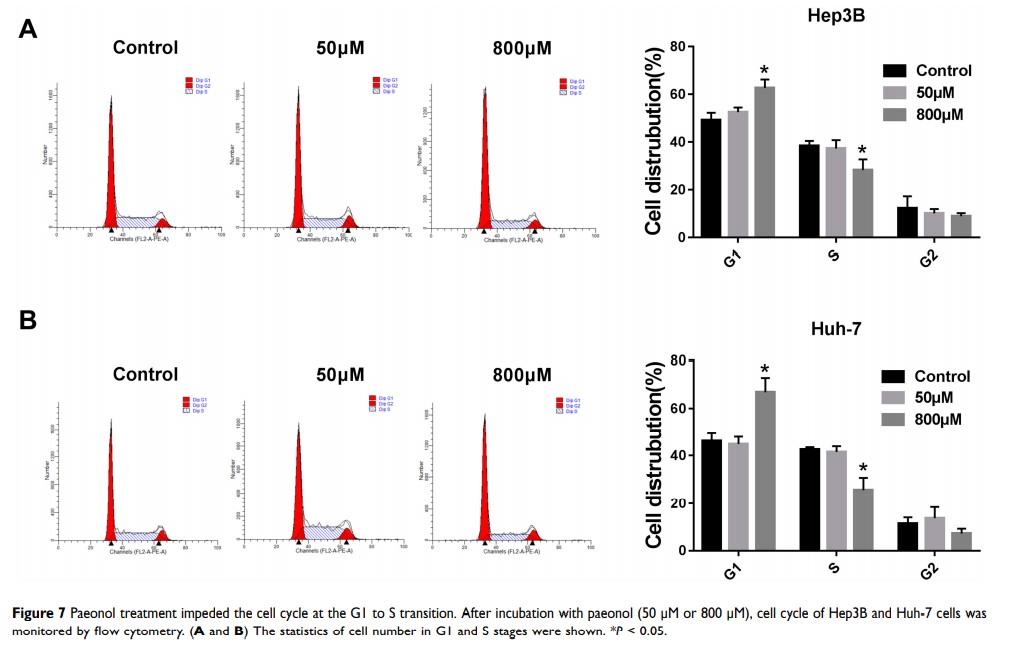
Conclusion: Paeonol impeded cell viability, migration and invasion and triggered apoptosis by regulating miR-21-5p/KLF6 axis in HCC cells. Xenograft assay confirmed that paeonol inhibited tumor growth through miR-21-5p/KLF6 axis in HCC in vivo.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, paeonol, miR-21-5p, KLF6