108384
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

雷公藤内酯酮可调节 MAPK 信号通路,并通过人骨肉瘤细胞中内质网应激介导的细胞凋亡发挥抗癌作用
Authors Zheng L, Fang S, Hui J, Rajamanickam V, Chen M, Weng Q, Wu X, Zhao Z, Ji J
Received 20 April 2020
Accepted for publication 10 June 2020
Published 17 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 5919—5929
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S258203
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Background: Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary malignancy arise from bone and is one of the causes of cancer-related deaths. Triptonide (TN), a diterpenoid epoxide presented in Tripterygium wilfordii , is shown to possess a broad spectrum of biological properties.
Methods: In this study, we investigate the growth inhibitory effect of TN against human OS cells and its underlying molecular mechanism of action.
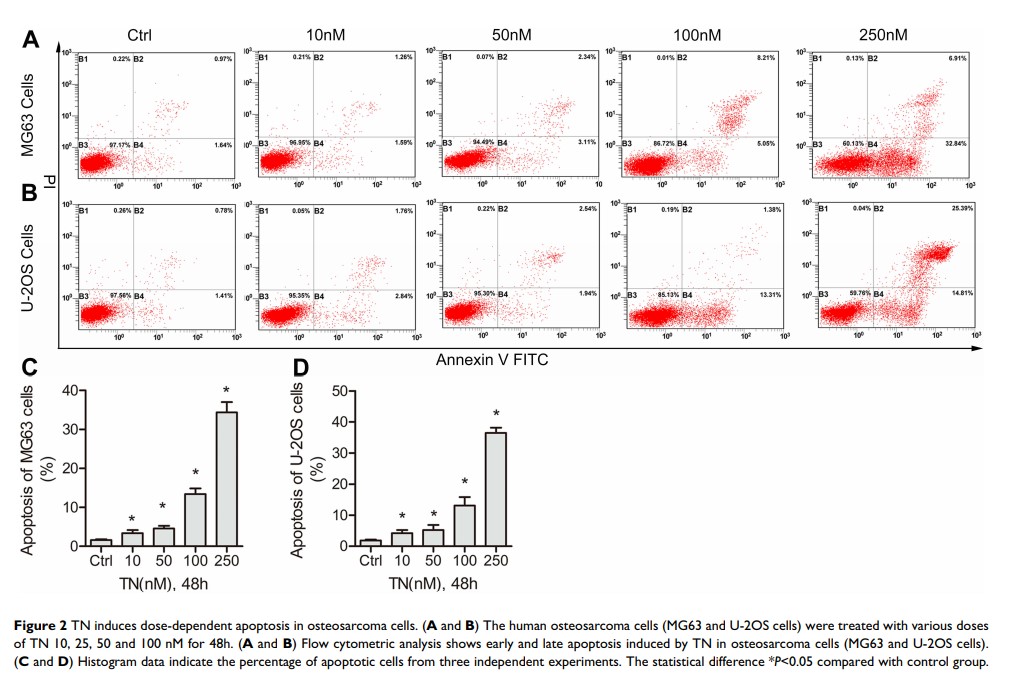
Results: Findings of our in vitro study revealed that TN exhibited a dose-dependent cytotoxic effect in MG63 and U-2OS cells. ROS-mediated cytotoxic effect was achieved in OS cells treated with TN which was reversed upon NAC treatment. Significantly, increased expression of PERK, p-EIF2, GRP78, ATF4 and CHOP in TN-treated OS cells unfolds the molecular mechanism of TN targets ER stress-mediated apoptosis. Modulation of ERK MAPK pathway was also observed as evidenced by the increased phosphorylation of ERK (p-ERK) and p-p38 in TN-treated OS cells.
Conclusion: Altogether, the outcome of the study for the first time revealed that TN exhibited its potential chemotherapeutic effects through ROS-mediated ER stress-induced apoptosis via p38 and ERK MAPK signaling pathways.
Keywords: osteosarcoma, triptonide, ER stress, apoptosis, MAPK signaling