108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

虫草素通过调节 TGF-β 活性和自噬来减轻前交叉韧带切断术(ACLT)引起的膝骨关节炎
Authors Tao XM, Liu PF, Gu HY, Lian DB, Gao L, Tao WW, Yan D, Zhao B
Received 29 February 2020
Accepted for publication 31 May 2020
Published 17 July 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2809—2817
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S251893
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
Introduction: Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent articular disease in the elderly. We aimed to explore the role of cordycepin (COR) in the progression and development of osteoarthritis and its correlation with TGF-β activity and autophagy.
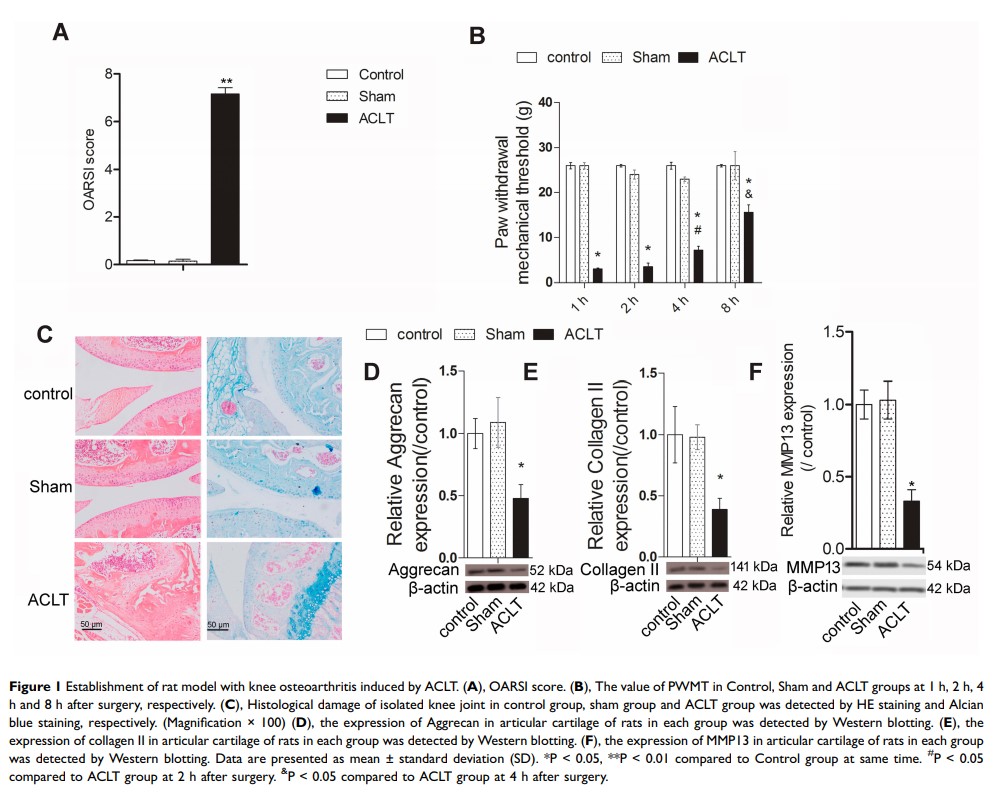
Methods: Sprague Dawley rats were induced by anterior cruciate ligament transection (ACLT) to establish knee osteoarthritis model. To investigate the role of COR in knee osteoarthritis, rats were injected with 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg of COR before joint surgery. After surgery, paw withdrawal mechanical threshold (PWMT) was performed. HE staining and Alcian blue staining were carried out to detect cartilage damage. ELISA was used to detect the level of TGFβ in the serum. Protein expression was analyzed by Western blotting.
Results: In this study, we found that the PWMT of rats with osteoarthritis induced by ACLT was decreased significantly, accompanied by obvious histological and cartilage damage. After different doses of COR treatment, the PWMT of osteoarthritis rats induced by ACLT was increased in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, compared with the control group, COR treatment also reversed the effect of ACLT on cartilage injury in rats. Furthermore, the level of TGF-β in serum of ACLT rats was increased significantly, which may be related to the overexpression of TGF-β R1. However, the increase of serum TGF-β level in ACLT rats was reversed by COR treatment in a dose-dependent manner. It is worth noting that TGF-β overexpression reduced the proportion of autophagy-related protein LC3-II/I, thus inhibiting autophagy. In order to further confirm the effect of TGF-β on autophagy, TGF-β was overexpressed or the autophagy inhibitor 3-MA was applied. The results showed that TGF-β overexpression and 3-MA treatment reversed the effect of COR on autophagy.
Conclusion: In summary, our findings declared that COR alleviated ACLT-induced osteoarthritis pain and cartilage damage by inhibiting TGF-β activity and inducing autophagy in rat model with knee osteoarthritis.
Keywords: cordycepin, anterior cruciate ligament transection, osteoarthritis, TGF-β, autophagy, in vivo