108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

丹参酮 IIA 通过 miR-133a-3p/EGFR 轴调节心肌细胞 H9c2 的增殖和凋亡,以改善 CAD 的进展
Authors Xu H, Li H, Zhu P, Liu Y, Zhou M, Chen A
Received 14 January 2020
Accepted for publication 16 June 2020
Published 20 July 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2853—2863
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S245970
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Manfred Ogris
Background: Coronary artery disease (CAD) leads to the highest mortality worldwide, seriously threatening human health. Tanshinone IIA (Tan IIA), which could be extracted from Danshen, is applied in the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. MicroRNAs (miRNAs, miRs) play pivotal roles in cell proliferation and cell apoptosis of the cardiovascular system. The aim of the present study was to explore the role of Tan IIA in CAD in vitro and the underlying molecular mechanism.
Methods: Real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blot were used for the detection of miRNA/mRNA and protein, respectively. Target genes of miR-133a-3p were searched in TargetScan, and the targeting relationship was verified by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Cell proliferation was determined using a Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and EdU labeling. Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry and TUNEL staining.
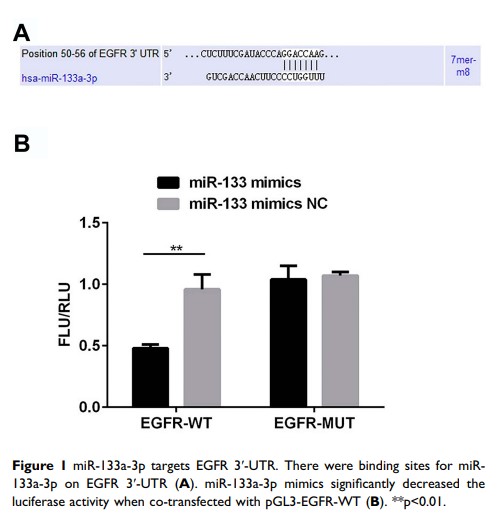
Results: In the present study, lower miR-133a-3p level and higher epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; the target of miR-133a-3p) level were found in H2O2-induced H9c2 cells. In addition, Tan IIA upregulated miR-133a-3p and downregulated EGFR expression. Moreover, Tan IIA promoted cell proliferation and suppressed apoptosis and enhanced G0/G1, which was reversed by miR-133a-3p inhibitor, while siRNA-EGFR abolished the effects induced by miR-133a-3p in H2O2-induced H9c2 cells.
Conclusion: Tan IIA reversed H2O2-induced cell proliferation reduction, cell apoptosis induction, and G0/G1 arrest reduction in H9c2 cells by miR-133a-3p/EGFR axis. The findings suggested a potential molecular basis of Tan IIA in treating patients with CAD.
Keywords: tanshinone IIA, coronary artery disease, miR-133a-3p, EGFR