108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

间充质基质细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡对脑缺血再灌注引起的神经功能损伤的神经保护作用:AMPK 和 JAK2/STAT3/NF-κB 信号通路调节的关键作用
Authors Han M, Cao Y, Xue H, Chu X, Li T, Xin D, Yuan L, Ke H, Li G, Wang Z
Received 8 February 2020
Accepted for publication 3 June 2020
Published 20 July 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2865—2876
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S248892
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
Introduction: Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (CIRI) is the main factor that leads to poor prognosis of cerebral ischemia. Apoptosis has been shown to occur during the process of CIRI. Extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs-EVs) have shown broad potential for treating brain dysfunction and eliciting neuroprotective effects after stroke through neurogenesis and angiogenesis. However, the mechanism of action of extracellular vesicles during CIRI is not well known.
Methods: A middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model was induced by the modified Longa method, and MSCs-EVs were injected via the tail vein.
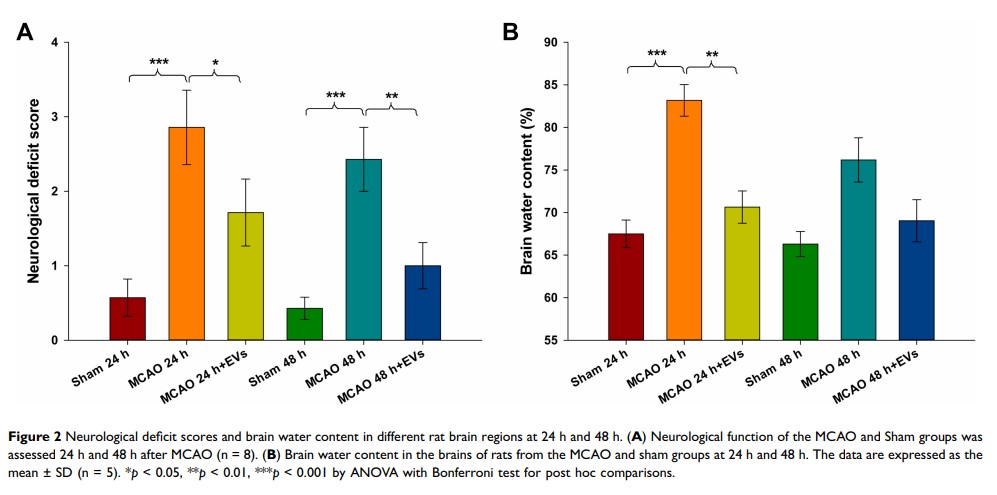
Results: Our results showed that MSCs-EVs significantly alleviated neurological deficits, reduced the volume of cerebral infarction and brain water content, improved pathological lesions in cortical brain tissue, and attenuated neuronal apoptosis in the cortex at 24 h and 48 h after MCAO in rats. Western blotting analysis showed that MSCs-EVs significantly upregulated p-AMPK and downregulated p-JAK2, p-STAT3 and p-NF-κB. In addition, an AMPK pathway blocker reversed the effect of MSCs-EVs on brain damage.
Conclusion: These results indicate that MSCs-EVs protected MCAO-injured rats, possibly by regulating the AMPK and JAK2/STAT3/NF-κB signaling pathways. This study supports the use of MSCs-EVs as a potential treatment strategy for MCAO in the future.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles, cerebral ischemia reperfusion, neuroprotection, AMPK, nuclear factor κB, JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway