108552
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

WHSC1 通过激活 mTORC1 信号传导促进肝细胞癌的细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Dai J, Jiang L, Qiu L, Shao Y, Shi P, Li J
Received 6 February 2020
Accepted for publication 5 July 2020
Published 20 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7033—7044
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S248570
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
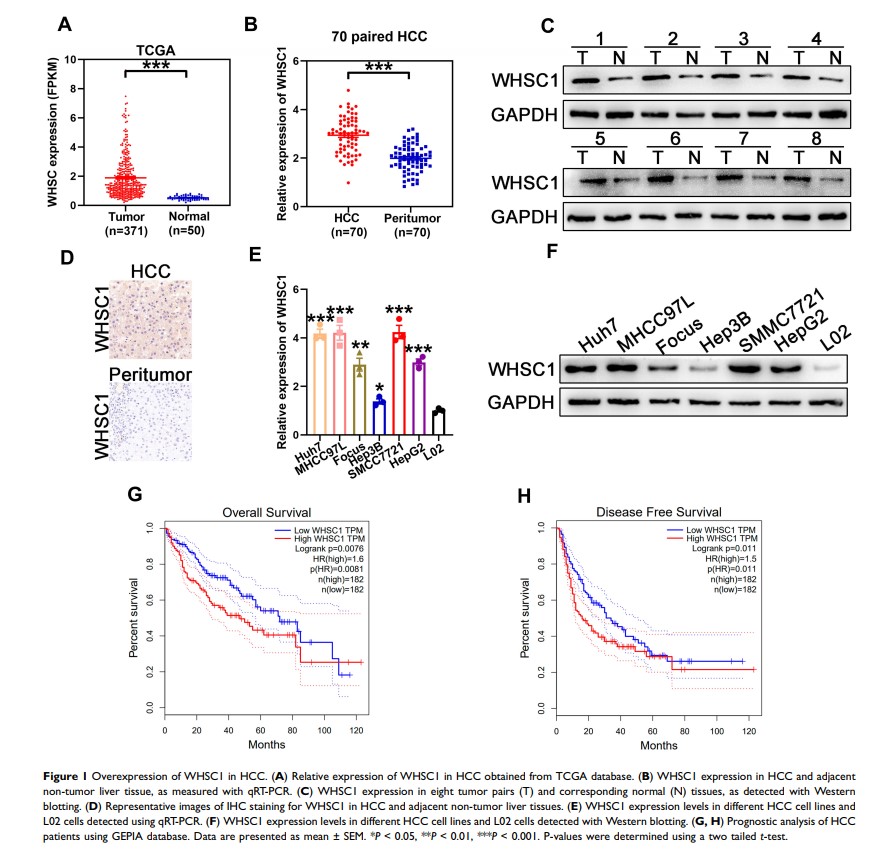
Background: Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate gene-1 (WHSC1) plays key regulatory roles in cancer development and progression. However, its specific functions and potential mechanisms of action remain to be described in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Materials and Methods: WHSC1 expression in HCC was evaluated using The Cancer Genome Atlas and verified in HCC tissues and cell lines using qRT-PCR, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. Functional assays were performed to explore the role of WHSC1 in HCC progression. Immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry, co-immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry were conducted to evaluate the interaction between WHSC1 and prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit beta (P4HB). Pathway enrichment was performed using gene set enrichment analysis.
Results: WHSC1 was markedly overexpressed in HCC tissues and cell lines. The level of expression was strongly associated with adverse clinicopathological characteristics. Survival analyses revealed that WHSC1 upregulation predicted poor overall survival and higher recurrence rates in patients with HCC. Functional studies revealed that WHSC1 significantly stimulated HCC proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and in vivo. WHSC1 was shown to interact with P4HB to stimulate P4HB expression and subsequently activate mTOR1 signaling.
Conclusion: We determined the oncogenic role of WHSC1 in HCC, via P4HB interaction, which activates mTOR1 signaling, and identified WHSC1 as a promising therapeutic target for HCC.
Keywords: apoptosis, metastasis, P4HB, poor prognosis, hepatocarcinogenesis