108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

STEAP4 抑制 HIF-1α/PKM2 信号传导并减少高糖诱导的视网膜血管内皮细胞凋亡
Authors Liu L, Xu H, Zhao H, Jiang C
Received 27 February 2020
Accepted for publication 29 April 2020
Published 20 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2573—2582
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S251663
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Juei-Tang Cheng
Background: Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a vascular lesion induced by high glucose. STEAP4 is an indispensable membrane protein, which is closely related to hyperglycemic-induced cell inflammation and injury, while STEPT4 has not been studied in hyperglycemic-induced retinal vascular endothelial cell injury.
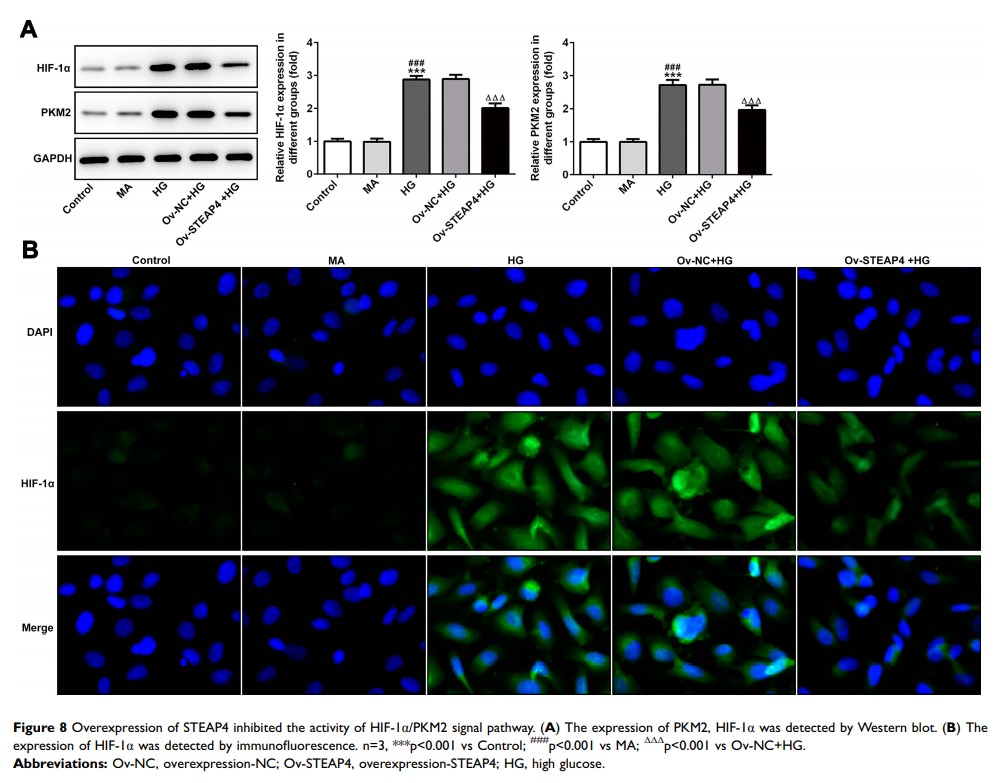
Methods: The expression of STEAP4 was detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot. CCK-8 was used to detect cell survival. STEAP4 was overexpressed by cell transfection. The expressions of cytokines TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, ICAM-1, MDA, SOD and ROS were detected by ELISA. Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. The expressions of proteins associated with cell damage VEGF, KLF2, eNOS and apoptosis-related proteins Bax, cleaved caspase3 and Bcl2 were detected by Western blot. Finally, the expressions of HIFα and PKM2 were detected by immunofluorescence and Western blot.
Results: The expression of STEAP4 in hyperglycemic-induced retinal vascular endothelial cells (HRCECs) decreased gradually. Overexpression of STEAP4 reduced inflammation and apoptosis of HRCECs and improved dysfunction of them. Meanwhile, overexpression of steap4 inhibited the expression of HIF-1α/PKM2 signal.
Conclusion: STEAP4 can be a potential therapeutic target for diabetic retinopathy by inhibiting HIF1/PKM2 signaling to reduce hyperglycemic-induced retinal cell apoptosis.
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy, STEAP4, HIF-1α/PKM2, HG-induced retinal vascular endothelial cells