108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在特定 ICU 中的 III 期重度新冠病毒 COVID-19 患者:临床特征和死亡率预测因素
Authors Wang ZH, Shu C, Ran X, Xie CH, Zhang L
Received 16 May 2020
Accepted for publication 7 July 2020
Published 20 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 833—845
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S263095
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Marco Carotenuto
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a worldwide pandemic outbreak with a high mortality. Prognostic factors of critically ill patients with COVID-19 have not been fully elucidated yet.
Methods: In the present study, 59 patients with COVID-19 from the intensive care unit of the Caidian Branch of Tongji Hospital were enrolled. Epidemiological, demographic, clinical, laboratory, radiological, treatment data, and clinical outcomes were collected. Prognostic factors were statistically defined.
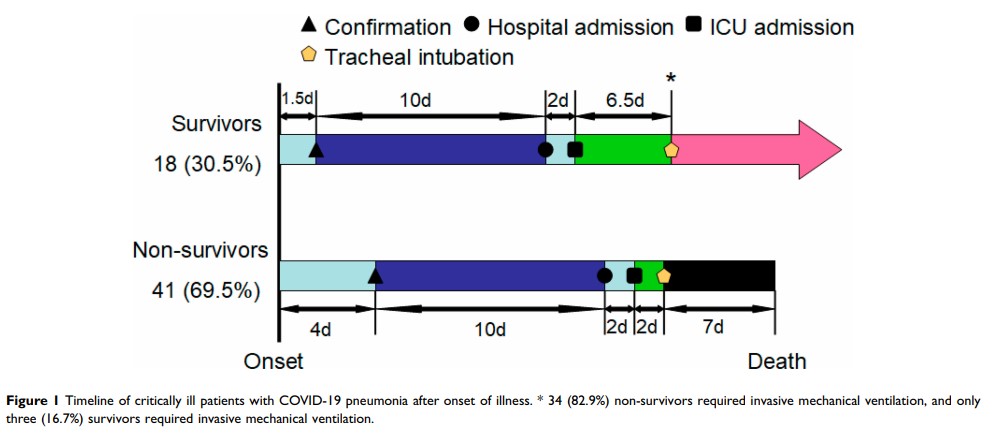
Results: Of the 59 patients studied (67.4± 11.3 years), 38 patients were male, 51 had underlying diseases, and 41 patients died during admission. Compared with the survivors, the deceased patients were of older age, had more smoking history, severer fatigue, and diarrhea, a higher incidence of multiple organ injuries, more deteriorative lymphopenia and thrombocytopenia, remarkably impaired cellular immune response, and strengthened cytokine release. Age higher than 70 (OR=2.76, 95% CI=1.45– 5.23), arrhythmia (OR=4.76, 95% CI=1.59– 14.25), and a Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score above 4 (OR=5.16, 95% CI=1.29– 20.55) were identified as risk factors for mortality of patients.
Conclusion: Critically ill COVID-19 patients aged higher than 70, arrhythmia, or a SOFA score above 4 have a high risk of mortality, and need prior medical intervention.
Keywords: severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2, pneumonia, critically ill, mortality, prognostic factor