108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA AGAP2-AS1/miR-628-5p/PTN 轴可调节胶质瘤细胞的增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡
Authors Yan Y, Wang Y, Liu Y, Chen T, Zhu Y, Li H, Kong F
Received 22 February 2020
Accepted for publication 13 June 2020
Published 20 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6059—6068
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S250890
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Bilikere Dwarakanath
Purpose: Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been reported to be involved in a variety of cancers, including glioma. However, the exact role and underlying mechanism of lncRNA AGAP2 antisense RNA 1 (AGAP2-AS1) in glioma have not yet been fully elucidated.
Methods: The expression levels of AGAP2-AS1, microRNA-628-5p (miR-628-5p) and pleiotrophin (PTN) were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion were detected by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, flow cytometry, transwell assay, respectively. Western blot assay was used to detect the protein level of PTN. The interaction between miR-628-5p and AGAP2-AS1 or PTN was predicted by bioinformatics software and confirmed by the dual-luciferase reporter and RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays. Murine xenograft model was established to confirm the role of AGAP2-AS1 in glioma progression in vivo.
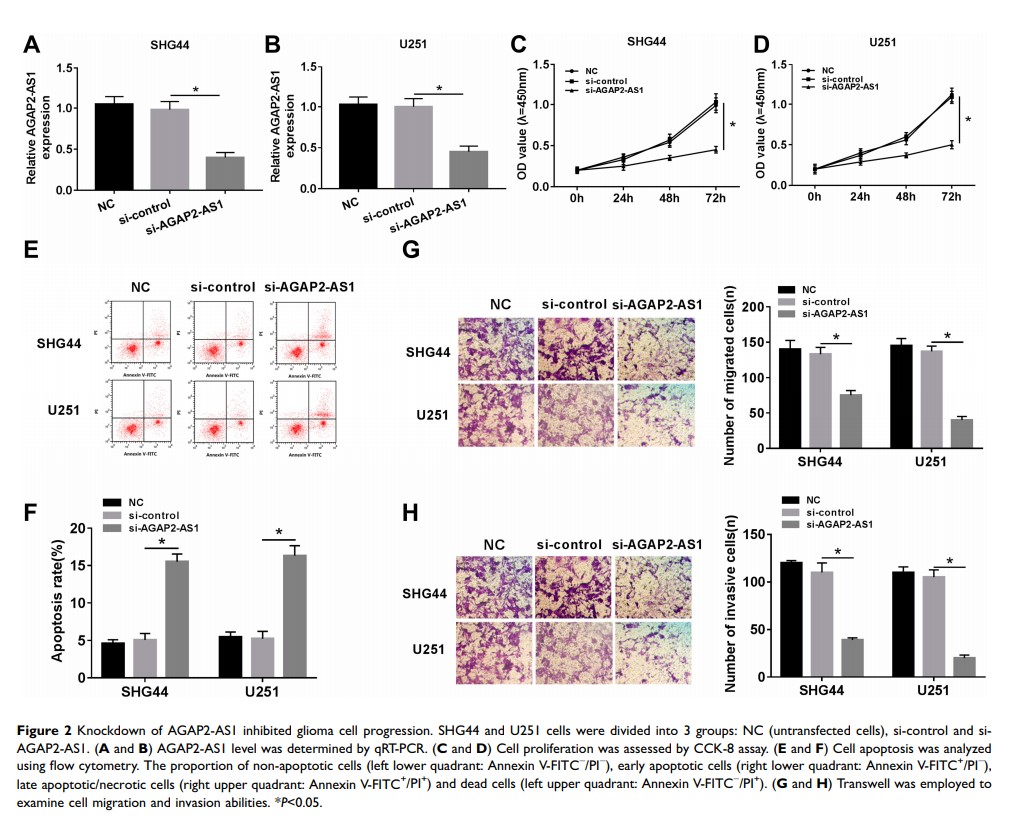
Results: AGAP2-AS1 expression was upregulated in glioma tissues and cells. Knockdown of AGAP2-AS1 inhibited the proliferation, migration and invasion, but facilitated apoptosis in glioma cells. Moreover, AGAP2-AS1 could directly bind to miR-628-5p and its overexpression reversed the anti-tumor effect of miR-628-5p restoration on the progression of glioma cells. In addition, miR-628-5p directly targeted PTN and its inhibition abolished the inhibitory effect of PTN knockdown on the progression of glioma cells. Furthermore, AGAP2-AS1 functioned as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) by sponging miR-628-5p to modulate PTN expression. Besides, AGAP2-AS1 depletion reduced tumor growth by upregulating miR-628-5p and downregulating PTN.
Conclusion: AGAP2-AS1 knockdown suppressed cell proliferation, migration and invasion but promoted cell apoptosis in glioma cells by regulating miR-628-5p/PTN axis, providing novel avenues for treatment of glioma.
Keywords: glioma, AGAP2-AS1, miR-628-5p, PTN, cell progression