108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

DHRS9 过表达对胰腺癌预后的影响
Authors Li H, Zhou J, Zhao F, Yu J, Xu L
Received 29 February 2020
Accepted for publication 24 June 2020
Published 20 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 5997—6006
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S251897
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Seema Singh
Purpose: Pancreatic cancer (PC) has poor prognosis despite systemic treatment. Dehydrogenase/reductase member 9 (DHRS9) has been reported to be involved in many events of tumorigenesis, but its prognostic impact in PC remains undetermined. Thus, this study aimed to explore the association between DHRS9 expression and the prognosis of PC and investigate the possible mechanism by which DHRS9 is involved in PC progression.
Patients and Methods: The study used data: from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and our institution to compare the DHRS9 expression between PC and adjacent normal tissues; from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and our institution to assess the clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of PC patients in high and low DHRS9 expression groups; and from TCGA to predict the potential mechanism of DHRS9 in PC. Western blot assay was used to identify DHRS9 expression in specimens collected from five patients who underwent surgery in our institute. Furthermore, immunohistochemistry (IHC) was then used to identify DHRS9 expression in the specimens of 109 patients who underwent surgery at our institute. Kaplan–Meier and Cox regression analyses were used to assess the prognostic significance of DHRS9 expression among PC patients.
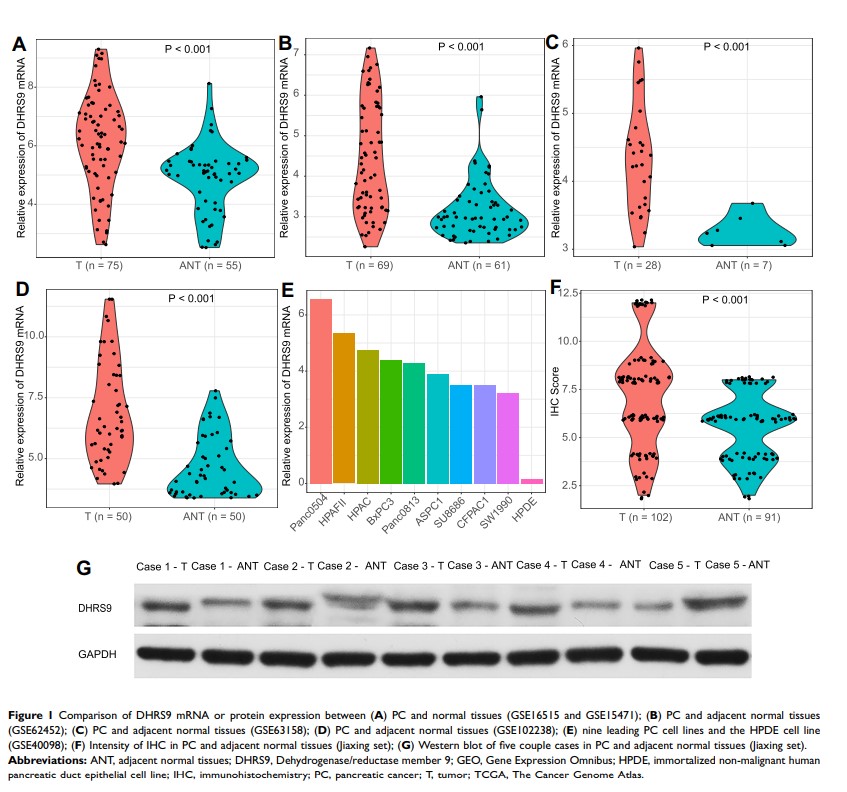
Results: All the IHC, Western blot, and GEO datasets indicated that compared to normal tissues, DHRS9 was significantly overexpressed in PC tissues. IHC results demonstrated that the strong intensity of DHRS9 expression was significantly correlated with vascular infiltration (P < 0.05). Further, high DHRS9 expression was identified as a prognostic risk factor for overall survival. Functional analysis of DHRS9 co-expressed genes indicated that DHRS9 was involved in mitogen-activated protein kinases/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK) signaling pathway.
Conclusion: DHRS9 is upregulated in PC tissue, and high DHRS9 expression is correlated with poor prognosis in PC. DHRS9 may affect the oncological process of PC through MAPK/ERK pathway.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer progression, prognosis, MAPK/ERK pathway, TCGA, GEO