108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

敲低 IKKβ 抑制柔脑膜转移小鼠模型的肿瘤发展和肺癌细胞的增殖
Authors Liu Y, Li Y, Li Z, Li C, He J, Bu H
Received 2 March 2020
Accepted for publication 24 June 2020
Published 20 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6007—6017
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S252184
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
Objective: This study will explore the role of IKKβ in the leptomeningeal metastasis (LM) of lung cancer cells.
Methods: In vitro studies were conducted in mouse Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells with IKKβ knockdown. Cell proliferation was explored using CCK-8 and tumor colony-forming assays. The expression of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway was detected by Western blot. Tumor cell apoptosis was identified through Western blot detection of Bax and Bcl-2. The migration of tumor cells was identified by a wound healing assay. In vivo studies used an LM mouse model developed by injecting LLC cells with or without IKKβ knockdown into the cisterna magna. Mouse brain and spinal samples were sectioned for hematoxylin and eosin staining.
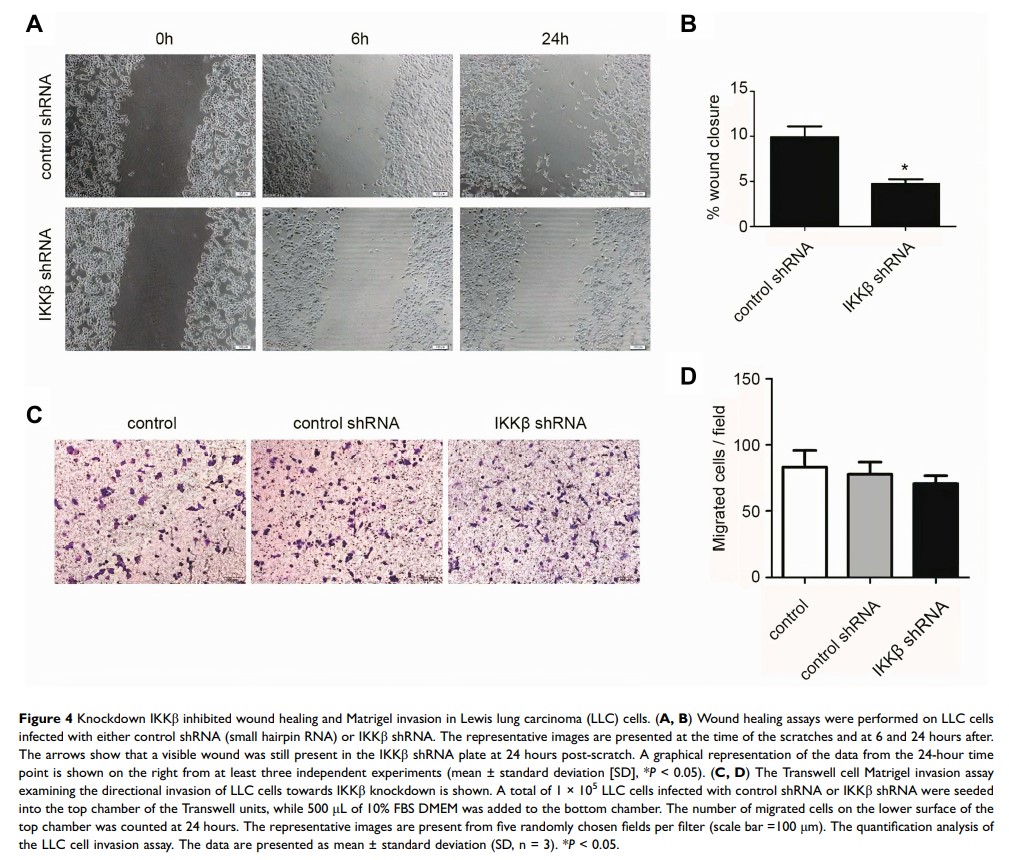
Results: In vitro: IKKβ knockdown inhibits tumor cell proliferation, initiates apoptosis, and attenuates cell migration. In vivo: IKKβ knockdown inhibits tumor growth in the LM mouse model. In addition, the in vitro results showed that IKKβ knockdown attenuated the expression of ERK phosphorylation in LLC cells.
Conclusion: Blocking the NF-κB signaling pathway by IKKβ knockdown in LLC cells inhibited tumor growth in the LM mouse model. IKKβ supports leptomeningeal tumor progression by promoting cancer cell proliferation and migration and inhibiting cancer cell apoptosis, and these actions may be correlated to ERK signaling.
Keywords: leptomeningeal metastasis, non-small-cell lung cancer, NF-κB signaling, IKKβ, shRNA