108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

下一代测序和 Ventana 免疫组化在检测 ALK 重排和预测一线 Crizotinib 对晚期非小细胞肺癌患者疗效方面的比较
Authors Zeng L, Li Y, Xu Q, Jiang W, Lizaso A, Mao X, Zhang Y, Yang N, Wang Z
Received 11 June 2020
Accepted for publication 9 July 2020
Published 22 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7101—7109
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S265974
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
Introduction: Reliable diagnostic approaches to detect ALK rearrangement are critical for selecting patients eligible for crizotinib therapy. This study aimed to compare next-generation sequencing (NGS) and Ventana immunohistochemistry (IHC) in evaluating ALK rearrangements and evaluate their impact on first-line crizotinib efficacy.
Patients and Methods: A total of 472 NSCLC patients were identified as ALK-positive by NGS and/or IHC between March 2014 and February 2020. The concordance of ALK detection, overall response rate (ORR), and progression-free survival (PFS) were analyzed for 319 patients who received front-line crizotinib.
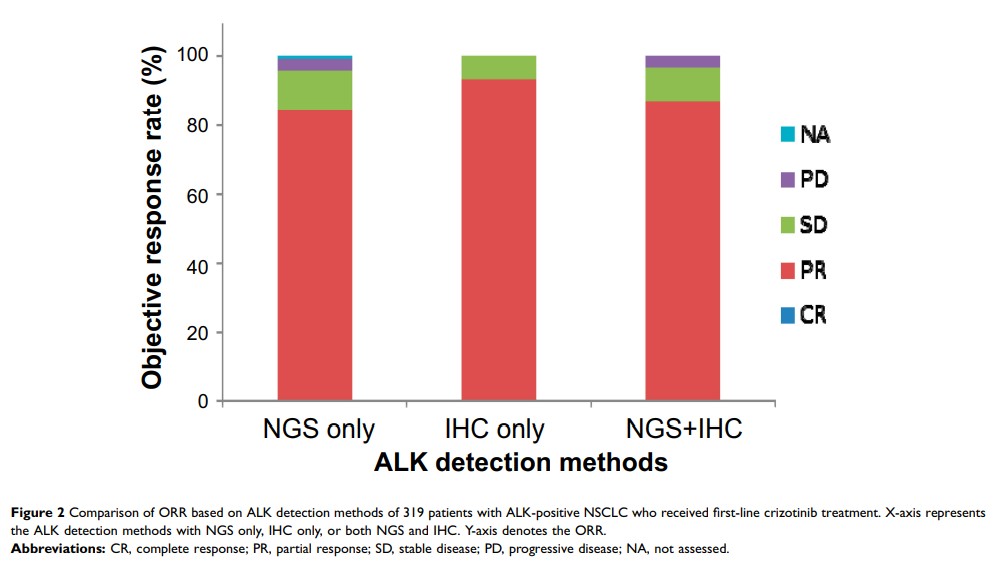
Results: First-line crizotinib (n=319) significantly prolonged PFS in comparison with chemotherapy (n=46; 12.0 vs 6.8 months; p< 0.0001). Of the 76 crizotinib-treated patients whose ALK status was assessed by both NGS and IHC, 78.9% of the patients had concordant ALK status (NGS-positive/IHC-positive), 18.4% patients were NGS-positive but IHC-negative, and 2 patients were IHC-positive but NGS-negative. Different detection assays confer no statistical difference in ORR and PFS with first-line crizotinib. The ORR in NGS only, IHC only, and both NGS and IHC was 84.3%, 90.1%, and 88.1%, respectively, while PFS was 11.4, 13.0, and 11.0 months, respectively. The ORR in NGS-positive/IHC-positive and NGS-positive/IHC-negative patients was 85.4% and 92.8%, respectively. Compared to NGS-positive/IHC-positive patients, those with NGS-positive/IHC-negative results had a trend of shorter PFS but statistical significance was not reached (mPFS, 5.9 months vs 11.5 months, p=0.43).
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that ALK status detected by NGS and/or IHC is reliable in identifying patients with ALK-positive NSCLC who will benefit from ALK inhibitor therapy.
Keywords: ALK status evaluation, ALK IHC, ALK inhibitor