108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

FOXCUT 通过激活 FOXC1/PI3K/AKT 信号通路促进大肠癌的增殖和侵袭
Authors Zhang X, Yi S, Xing G, Wu H, Zhu Y, Guo X, Zhang L
Received 12 May 2020
Accepted for publication 17 June 2020
Published 24 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6269—6278
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S259801
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most commonly diagnosed world cancer. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) serve important regulatory roles in tumorigenesis. However, the contributions of lncRNAs to human CRC remain largely unknown.
Material and Methods: FOXC1 and FOXCUT lncRNA expression levels were detected in a panel of paired specimens obtained from 48 patients’ tissues and cell lines with CRC using RT-qPCR. RNA interference was used to investigate potential correlations between FOXC1 and FOXCUT expression in HT29. Cell proliferation was assessed by MTT assay and EdU incorporation assay. The migration and invasion of CRC cells were detected by transwell assay. Western blot was applied to assess the protein expression and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
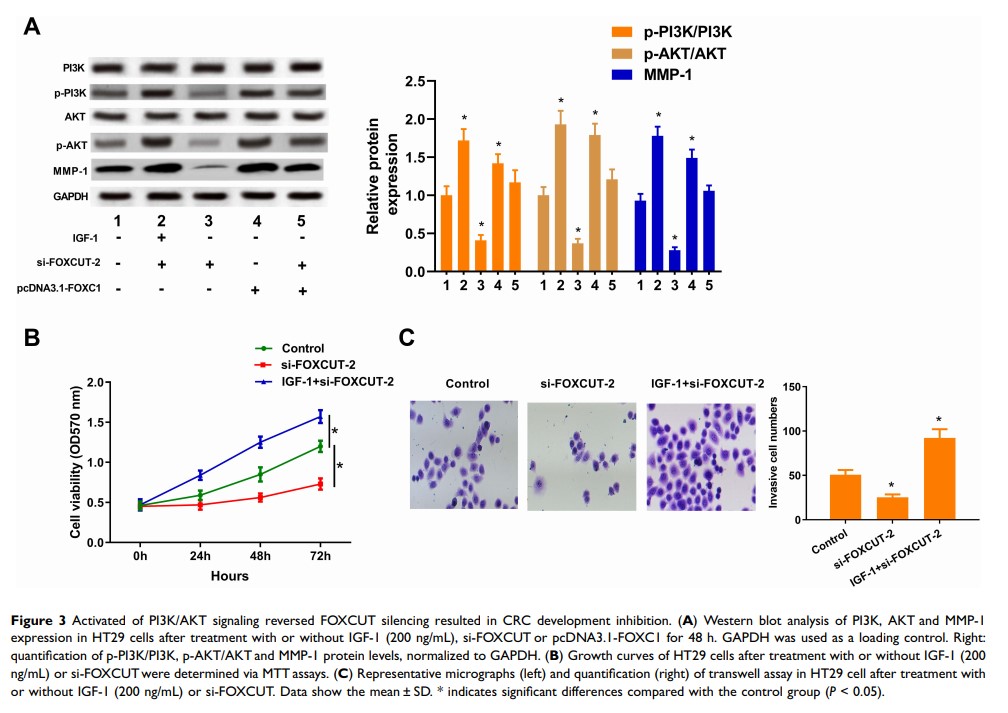
Results: In this study, a novel long noncoding RNA (FOXCUT) was frequently overexpressed in CRC tissues and cell lines. In addition, the expressions of FOXCUT and FOXC1 were positively correlated. When the expression of FOXCUT was downregulated by small interfering RNA (siRNA), the expression of FOXC1 was also decreased. Moreover, knockdown of FOXCUT significantly inhibited proliferation and invasion of CRC cell lines and resulted in downregulated expression of the matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1). Mechanistically, FOXCUT promotes the expression of FOXC1 to activate PI3K/AKT signaling pathway for its regulation of cell growth and proliferation.
Conclusion: In summary, our findings indicate that FOXCUT plays an important oncogenic role and may serve as a novel biomarker and therapeutic target in CRC progression.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, FOXCUT, FOXC1, proliferation, invasion