108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利拉鲁肽通过调节自噬减弱 APPswe/SH-SY5Y 细胞中 Aβ42 的生成
Authors Kong J, Wan L, Wang Y, Zhang H, Zhang W
Received 27 April 2020
Accepted for publication 28 June 2020
Published 27 July 2020 Volume 2020:16 Pages 1817—1825
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S260160
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yuping Ning
Objective: This study aimed to clarify whether liraglutide, a GLP-1 analogue, can ameliorate Aβ pathology through the regulation of autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and to explore the related mechanisms thereof.
Methods: We used SH-SY5Y cells transiently transfected with APP695swe plasmid as an AD cellular model. Transfected cells were treated with liraglutide for 24 h in the presence or absence of 3-MA. Autophagy markers and the Aβ level were then evaluated by Western blot and ELISA. We also investigated the potential involvement of mTOR and JNK pathway in liraglutide-mediated autophagy.
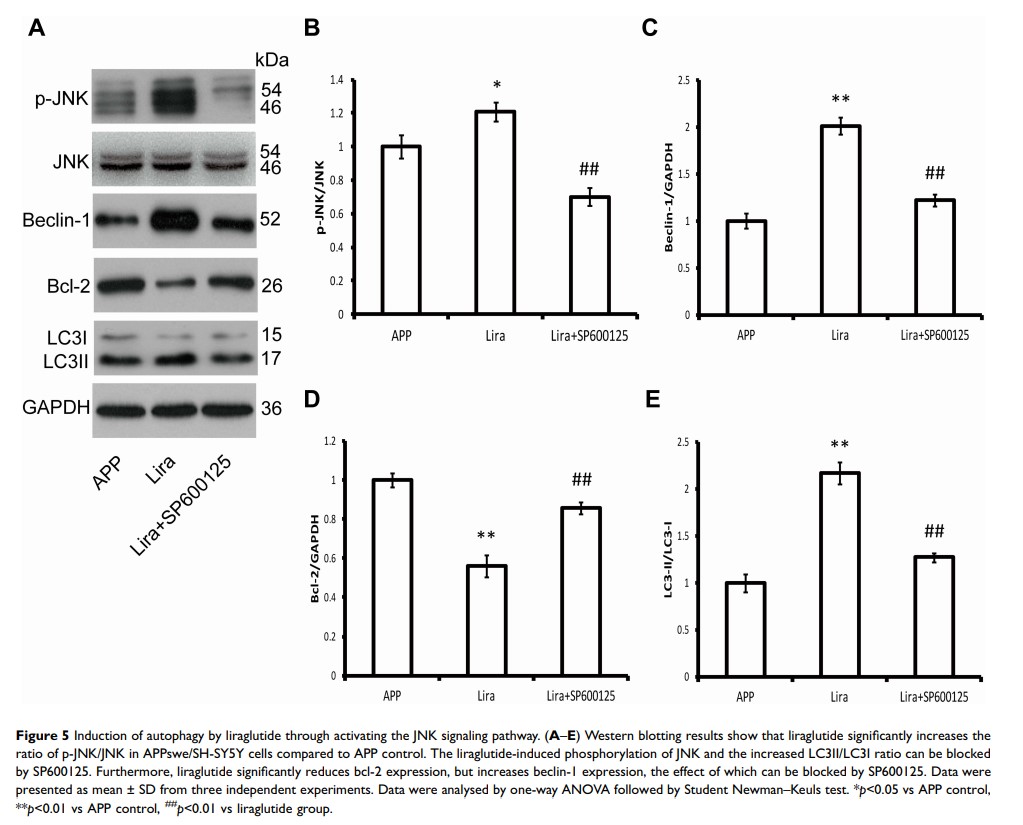
Results: Our results showed that liraglutide reduced Aβ 42 generation and enhanced autophagy in APPswe/SH-SY5Y cells; however, these effects could be counteracted with 3-MA. Furthermore, our data showed that liraglutide-induced autophagy does not follow the mTOR pathway. Liraglutide might promote autophagy in APPswe/SH-SY5Y cells by activating the JNK pathway and inhibiting the beclin-1/bcl-2 complex.
Conclusion: Here, we report a novel mechanism underlying liraglutide-attenuated Aβ 42 generation through the activation of autophagy in AD cellular model.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, glucagonlike peptide 1, autophagy, Aβ, JNK