108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Soluplus 介导的薯蓣皂苷配基无定形固体分散体具有高溶解度和高稳定性:开发、表征和口服生物利用度
Authors Liu P, Zhou J, Chang J, Liu X, Xue H, Wang R, Li Z, Li C, Wang J, Liu C
Received 11 March 2020
Accepted for publication 6 July 2020
Published 27 July 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 2959—2975
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S253405
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yan Zhu
Background and Purpose: The traditional Chinese medicine, diosgenin (Dio), has attracted increasing attention because it possesses various therapeutic effects, including anti-tumor, anti-infective and anti-allergic properties. However, the commercial application of Dio is limited by its extremely low aqueous solubility and inferior bioavailability in vivo. Soluplus, a novel excipient, has great solubilization and capacity of crystallization inhibition. The purpose of this study was to prepare Soluplus-mediated Dio amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs) to improve its solubility, bioavailability and stability.
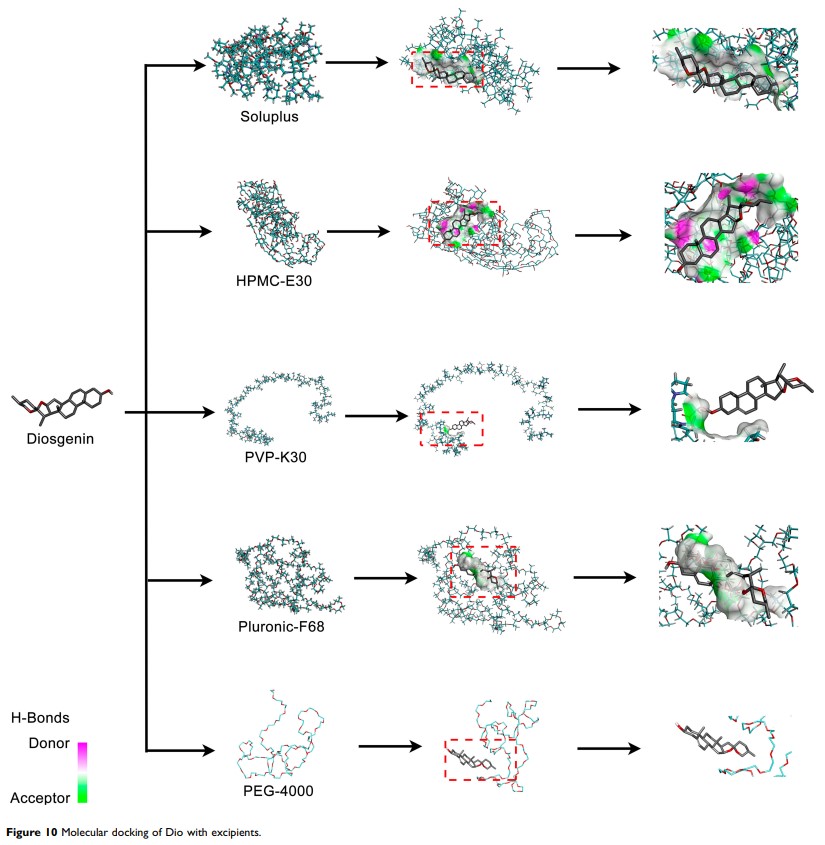
Methods: The crystallization inhibition studies were firstly carried out to select excipients using a solvent shift method. According to solubility and dissolution results, the preparation methods and the ratios of drug to excipient were further optimized. The interaction between Dio and Soluplus was characterized by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) and molecular docking. The pharmacokinetic study was conducted to explore the potential of Dio ASDs for oral administration. Furthermore, the long-term stability of Dio ASDs was also investigated.
Results: Soluplus was preliminarily selected from various excipients because of its potential to improve solubility and stability. The optimized ASDs significantly improved the aqueous solubility of Dio due to its amorphization and the molecular interactions between Dio and Soluplus, as evidenced by dissolution test in vitro, DSC, FT-IR spectroscopy, SEM, PXRD and molecular docking technique. Furthermore, pharmacokinetic studies in rats revealed that the bioavailability of Dio from ASDs was improved about 5 times. In addition, Dio ASDs were stable when stored at 40°C and 75% humidity for 6 months.
Conclusion: These results indicated that Dio ASDs, with its high solubility, high bioavailability and high stability, would open a promising way in pharmaceutical applications.
Keywords: diosgenin, amorphous solid dispersions, solubility, bioavailability, stability