108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血清 miR-503 是区分代谢型健康肥胖与代谢型不健康肥胖的候选生物标志物
Authors Yue HQ, Zhou YH, Guo Y, Tang CY, Wang F, Zhou HD
Received 19 May 2020
Accepted for publication 8 July 2020
Published 27 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 2667—2676
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S262888
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ming-Hui Zou
Purpose: Overweight and obesity are associated with metabolic diseases. However, a subgroup of the overweight/obese population does not present metabolic abnormalities. Hence, there is an urgent need to identify biomarkers that can distinguish different obesity phenotypes and metabolic status.
Patients and Methods: A total of 98 individuals were divided into three groups: metabolically healthy normal weight (MHNW), metabolically healthy obese (MHO), and metabolically unhealthy obese (MUO). Participants were evaluated for anthropometric and biochemical parameters and serum BMPR1A concentration and miR-503 level. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and logistic regression analysis were performed.
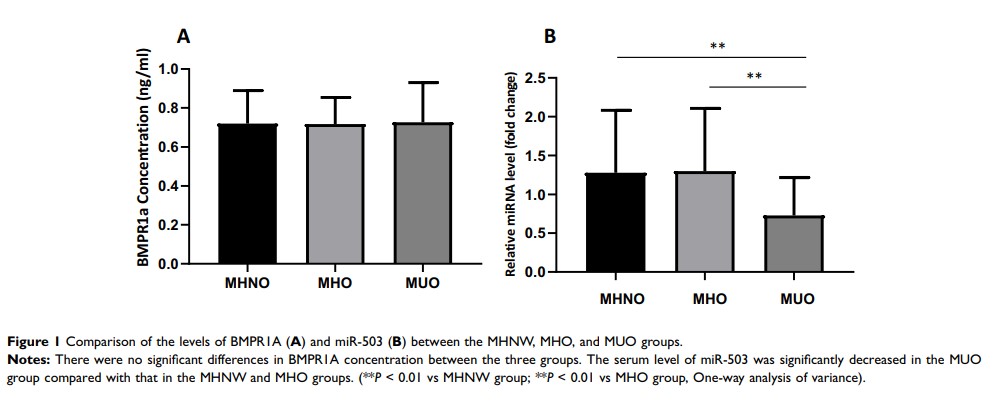
Results: The level of miR-503 was significantly higher in the MHO group compared with that in the MUO group, but no difference was observed between the MHNW and MHO groups. Meanwhile, no significant differences in serum BMPR1A concentration were observed between the three groups. ROC curve analysis showed that miR-503 could be used as a marker to distinguish the MUO from the MHO. Logistic regression analysis suggested that miR-503 was an important related factor associated with an unhealthy metabolic state in overweight/obese subjects.
Conclusion: miR-503 can be considered as a suitable biomarker to distinguish between the MUO and MHO, which may be a related factor for the incidence of metabolic disorders in overweight/obese subjects.
Keywords: micro RNA, metabolic syndrome, diagnosis