108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PD-L1 在肺腺癌中:对 18F-FDG PET/CT 作用的见解
Authors Cui Y, Li X, Du B, Diao Y, Li Y
Received 4 April 2020
Accepted for publication 20 June 2020
Published 27 July 2020 Volume 2020:12 Pages 6385—6395
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S256871
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Eileen O'Reilly
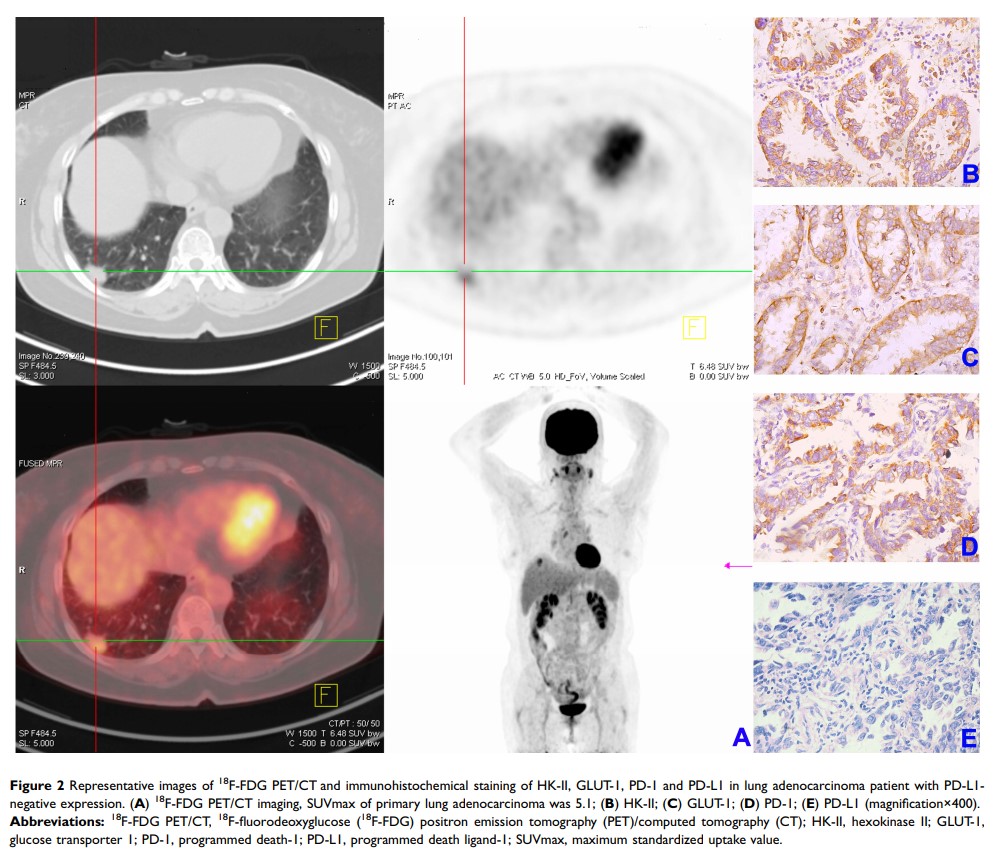
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the role of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) in expression of tumor programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression and prognostic significance of 18F-FDG PET/CT at different PD-L1 status in patients with lung adenocarcinoma.
Patients and Methods: Seventy-three patients with primary lung adenocarcinoma who received 18F-FDG PET/CT before treatment were retrospectively included in this study. Expression of tumor PD-L1, programmed death-1 (PD-1) and glucose metabolic parameters were evaluated.
Results: Tumor PD-L1 expression was positively correlated with maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), total lesion glycolysis (TLG), hexokinase II (HK-II) and glucose transporter 1 (GLUT-1) (P < 0.0001 for all). SUVmax was a unique independent predictor of tumor PD-L1 expression, with an optimal cut-off value of 9.5. For all the patients, tumor stage (P< 0.001) and SUVmax (P =0.009) were independent prognostic indicators of disease-free survival (DFS)/progression-free survival (PFS) while carcino-embryonic antigen (CEA) (P =0.003), Ki67 (P =0.042), PD-L1 (P =0.048) and TLG (P =0.004) were independent prognostic indicators of overall survival (OS). Tumor stage (P =0.004) and SUVmax (P =0.022) were independent prognostic indicators of DFS/PFS while TLG (P =0.012) and CEA (P =0.045) were independent prognostic indicators of OS in the PD-L1-positive group. In the PD-L1-negative group, tumor stage (P =0.002) and CEA (P =0.006) were unique independent prognostic indicators of DFS/PFS and OS, respectively.
Conclusion: 18F-FDG PET/CT may potentially predict tumor PD-L1 expression and play a role in predicting prognosis of PD-L1/PD-1 immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose, positron emission tomography, programmed death ligand-1, lung adenocarcinoma, prognosis