108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过代谢组学找到胃癌腹膜转移的生物标志物
Authors Pan G, Ma Y, Suo J, Li W, Zhang Y, Qin S, Jiao Y, Zhang S, Li S, Kong Y, Du Y, Gao S, Wang D
Received 11 January 2020
Accepted for publication 19 June 2020
Published 27 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7199—7211
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S245663
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background and Objective: Metabolomics has recently been applied in the field of oncology. In this study, we aimed to use metabolomics to explore biomarkers in peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer.
Methods: Peritoneal lavage fluid (PLF) of 65 gastric cancer patients and related clinical data were collected from the First Hospital of Jilin University. The metabolic components were identified by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Total ion current (TIC) spectra, principal component analysis (PCA), and the Student’s t-test were used to identify differential metabolites in PLF. A support vector machine (SVM) was used to screen the differential metabolites in PLF with a weight of 100%. Cluster analysis was used to evaluate the similarity between samples. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to assess the diagnostic ability of the metabolites. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify potential risk factors for peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer.
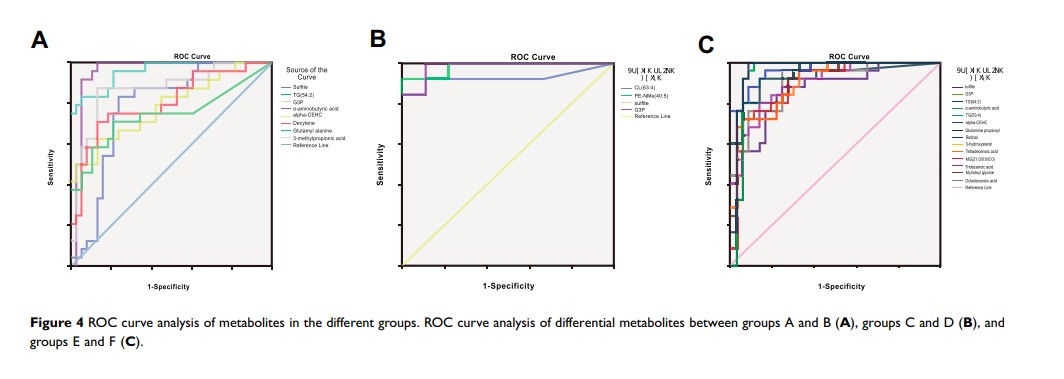
Results: We found the differential levels of PLF metabolites by LC-MS, TIC spectra, PCA and the t-test. Cluster analysis showed the co-occurrence of metabolites in the peritoneal metastasis group (p< 0.05). ROC analysis showed the diagnostic ability of metabolites (p< 0.05). Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses showed the potential independent risk factors for peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer patients (p< 0.05).
Conclusion: Through the statistical analysis of metabolomics, we found that TG (54:2), G3P, α-aminobutyric acid, α-CEHC, dodecanol, glutamyl alanine, 3-methylalanine, sulfite, CL (63:4), PE-NMe (40:5), TG (53:4), retinol, 3-hydroxysterol, tetradecanoic acid, MG (21:0/0:0/0:0), tridecanoic acid, myristate glycine and octacosanoic acid may be biomarkers for peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer.
Keywords: gastric cancer, metabolomics, peritoneal metastasis, diagnosis