108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

COVID-19 患者特殊人群的抗病毒剂治疗优化
Authors Li L, Wang X, Wang R, Hu Y, Jiang S, Lu X
Received 20 April 2020
Accepted for publication 9 July 2020
Published 28 July 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3001—3013
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S259058
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tuo Deng
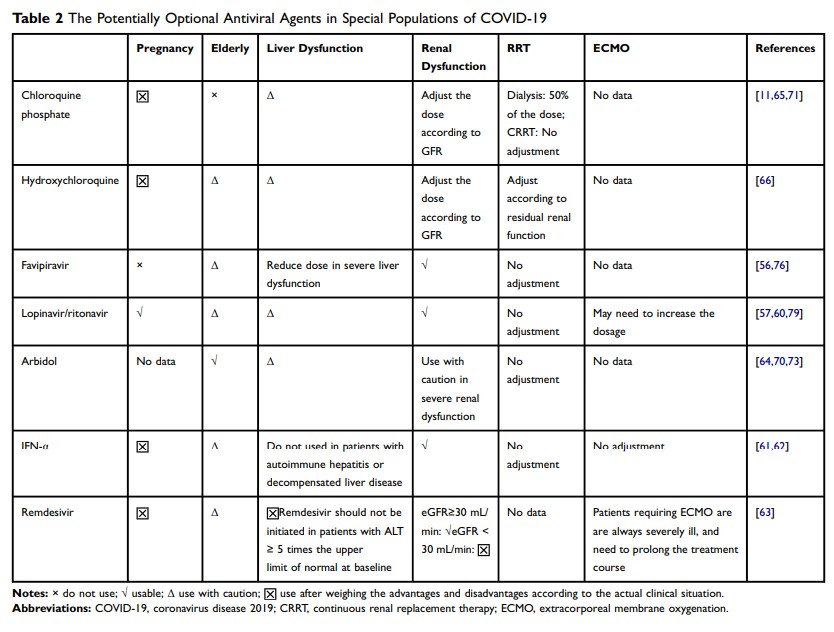
Abstract: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is now a global outbreak of disease. The antiviral treatment acts as one of the most important means of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Alteration of physiological characteristics in special populations may lead to the change in drug pharmacokinetics, which may result in treatment failure or increased adverse drug reactions. Some potential drugs have shown antiviral effects on SARS-CoV-2 infections, such as chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, favipiravir, lopinavir/ritonavir, arbidol, interferon alpha, and remedsivir. Here, we reviewed the literature on clinical effects in COVID-19 patients of these antiviral agents and provided the potential antiviral agent options for pregnant women, elderly patients, liver or renal dysfunction patients, and severe or critically ill patients receiving renal replacement therapy or ECMO after SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: coronavirus disease 2019, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, antiviral therapy, special population