108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-106b-5p 抑制 IRF1/IFN-β 信号传导,促进胶质母细胞瘤的 M2 型巨噬细胞极化
Authors Shi Y, Zhang B, Zhu J, Huang W, Han B, Wang Q, Qi C, Wang M, Liu F
Received 17 November 2019
Accepted for publication 6 July 2020
Published 30 July 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7479—7492
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S238975
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Jianmin Xu
Purpose: The microRNA (miRNA) profile changes in the tumor-associated macrophages. However, the role of miR-106b-5p in the glioblastoma-associated macrophages is poorly understood.
Materials and Methods: In our study, miR-106b-5p and M2 macrophage markers were detected by qRT-PCR and Western blotting in THP1 cells, with the conditioned medium from U251 cells or M2 macrophages in response to IL-4 stimulation and M1 macrophages stimulated by LPS and IFN-γ. IFN regulatory factor (IRF1) was identified as a target of miR-106b-5p in the glioma infiltrating macrophages by luciferase reporter assay. The molecular mechanisms involved in the miR-106b-5p-mediated regulation of M2 polarization were clarified by shRNA knockdown assay.
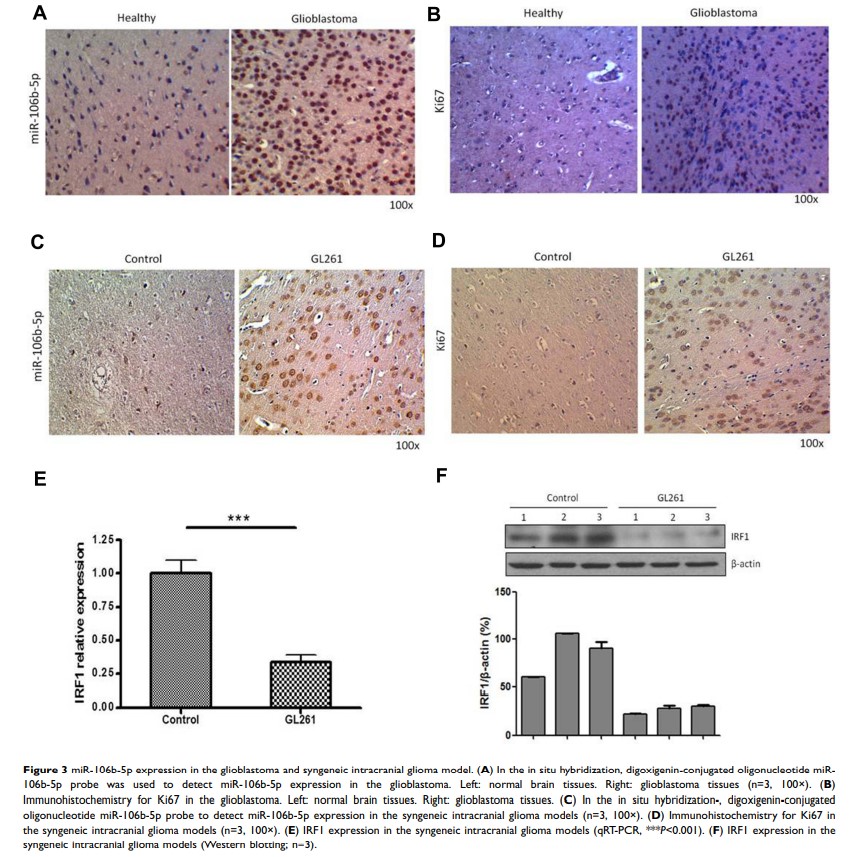
Results: Our results showed miR-106b-5p expression was upregulated in glioma-infiltrating macrophages. miR-106b-5p regulated M2 polarization of glioma infiltrating macrophages and enhanced the growth of glioma-infiltrating macrophages. IRF1 was identified as a target of miR-106b-5p. Furthermore, miR-106b-5p inhibited IRF1 expression by targeting IRF1/IFN-β pathway to promote M2 polarization of macrophages.
Conclusion: miR-106b-5p may inhibit IRF1/IFN-β signaling to promote M2 macrophage polarization of glioblastoma, and it may become a novel target for the treatment of glioblastoma.
Keywords: glioma, miR-106b-5p, IRF1/IFN-β, M2 macrophage polarization, glioma-associated microenvironment