108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

急性缺血性卒中患者的血浆白细胞介素-37 水平会升高,并可能与 3 个月的功能预后相关
Authors Zhang F, Zhu T, Li H, He Y, Zhang Y, Huang N, Zhang G, Li Y, Chang D, Li X
Received 7 September 2019
Accepted for publication 6 May 2020
Published 4 August 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1285—1294
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S230186
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Background: Interleukin-37 is a novel cytokine emerging as a natural suppressor of inflammatory responses. Inflammation and the immune response play important roles in acute ischemic stroke. This study aimed at evaluating the plasma levels and the association with 3-month outcomes of interleukin-37 in acute ischemic stroke patients.
Patients and Methods: In total, 152 consecutive patients with acute ischemic stroke and 45 healthy controls were included. Plasma interleukin-37 levels were determined in the first morning after admission using an enzyme-linked immunesorbent assay. The primary outcome was the 3-month functional outcome (modified Rankin Scale score > 2). Logistic regression was used to evaluate the risk and 3-month outcome of stroke according to plasma interleukin-37 level.
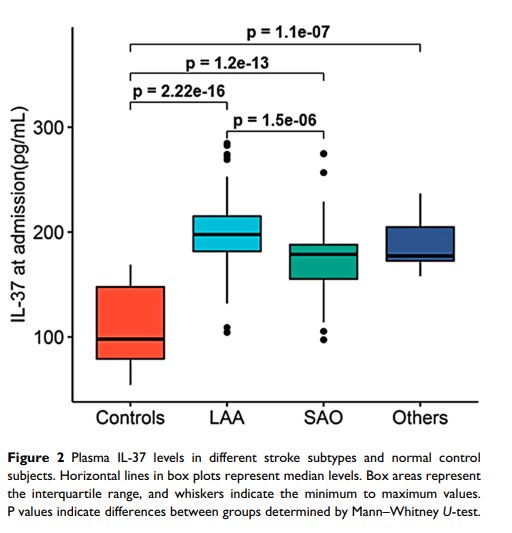
Results: Plasma interleukin-37 levels were significantly higher in the patients with acute ischaemic stroke than in the healthy controls (182.26 versus 97.89 pg/mL, p < 0.001). Patients with large-artery atherosclerosis had significantly higher IL-37 levels than those with small-artery occlusion (202.12± 35.82 versus 175.67± 33.71pg/mL, p < 0.001). Plasma interleukin-37 levels were positively correlated with National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale scores (r=0.521, p < 0.0001) and lesion volume (r=0.442, p < 0.0001). Ninety-four and 58 patients had favourable and unfavourable 3-month outcomes, respectively. Elevated plasma interleukin-37 levels were independently associated with unfavourable 3-month outcomes (adjusted odds ratio=1.033, p=0.001, 95% confidence interval: 1.015– 1.056).
Conclusion: Admission plasma interleukin-37 levels were significantly increased after acute ischemic stroke. Elevated interleukin-37 levels were independently associated with unfavourable 3-month prognoses in acute ischemic stroke patients. Further studies with other populations are needed.
Keywords: interleukin-37, acute ischemic stroke, functional outcome, prognosis