108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

碳纳米球可在前列腺癌中发挥与 4E-BP1 表达下调相关的抗肿瘤作用
Authors Dong W, Luo Y, Zhang G, Zhang H, Liang Y, Zhuo Y, Liang Y, Zou F, Zhong W
Received 15 April 2020
Accepted for publication 23 July 2020
Published 5 August 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 5545—5559
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S257522
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
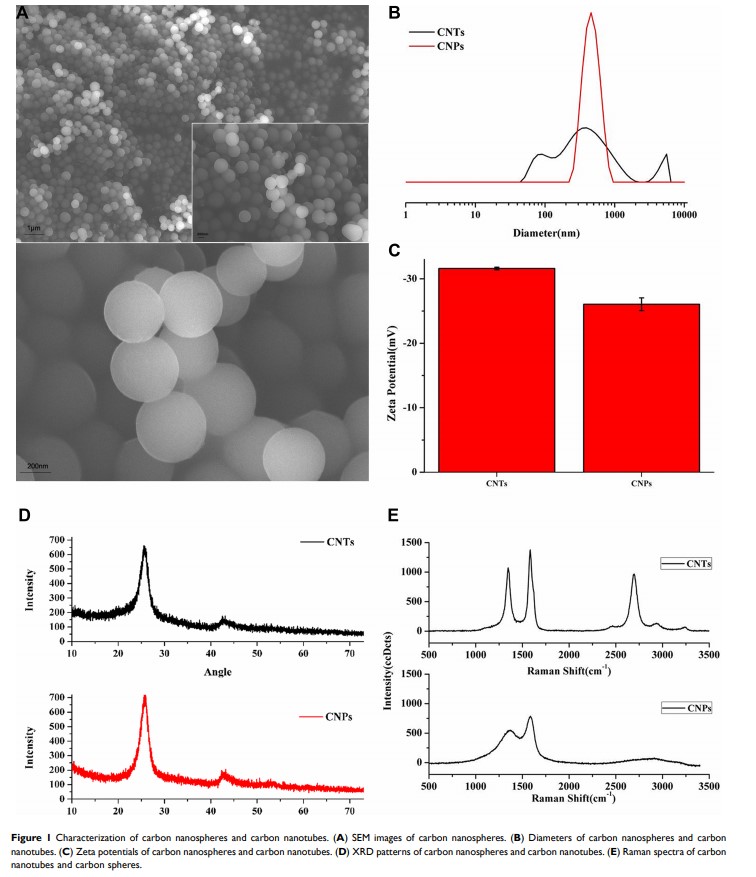
Introduction: Although carbon nanospheres (CNPs) are promising nanomaterials in cancer treatment, how they affect prostate cancer (PCa) remains unclear.
Methods: In this study, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Raman spectroscopy were used to confirm the successful synthesis of CNPs. CCK-8, flow cytometry, Transwell, wound healing, Western blot and immunohistochemistry (IHC) assays were performed to evaluate the antitumor effect of CNPs toward the two kinds of prostate cancer cell lines PC3 and DU145.
Results: Our results showed that CNPs inhibited cell growth, invasion, and migration and induced apoptosis and autophagy in PCa cells. Multifactor detection of a single Akt phosphorylation pathway and Western blot results suggested the suppression of 4E-BP1 in PCa cells after incubation with CNPs. The results from animal experiments also suggested the antitumor effect of CNPs and reduced 4E-BP1 expression in PCa tissue samples from BALB/c nude mice administered a local subcutaneous injection of CNPs.
Keywords: carbon nanosphere, prostate cancer, antitumor, 4E-BP1