108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

褪黑素通过调节 miR-26a-5p-NRSF 和 JAK2-STAT3 信号通路改善脑缺血-再灌注损伤的自噬、炎症和氧化应激,从而起保护作用
Authors Yang B, Zang LE, Cui JW, Zhang MY, Ma X, Wei LL
Received 21 May 2020
Accepted for publication 28 June 2020
Published 6 August 2020 Volume 2020:14 Pages 3177—3188
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S262121
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Anastasios Lymperopoulos
Background: Melatonin (MT) has potential protective effect on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury (CIRI), but its underlying regulatory mechanism has not been identified.
Purpose: This study aimed to explore the role of miR-26a-5p-neuron-restrictive silencing factor (NRSF/REST), Janus kinase-2 (JAK2)-signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) pathway in the protection mechanism of MT against CIRI in vivo and in vitro.
Methods: Sprague Dawley rats were induced with ischemia-reperfusion (IR) in vivo model; PC12 cells were induced with oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) in vitro model; and MT intervention was conducted before the model was established. The effect of MT on autophagy factors (LC3II/LC3I, P62), inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10) and oxidative stress indexes (MDA, GSHPx, SOD) was explored, and then the above three indexes were determined by real-time quantitative PCR, ELISA, and detection kit corresponding to oxidative stress indexes. The neuroprotective effect of MT pretreatment on brain IR injury was evaluated by neurological deficit scores and TUNEL method. The levels of miR-26a-5p and NRSF were detected by real-time quantitative PCR and Western blot, and the interaction between them was evaluated by dual luciferase report. The role of JAK2-STAT3 pathway in MT protection mechanism was verified by pathway blocker (AG490) and Western blot.
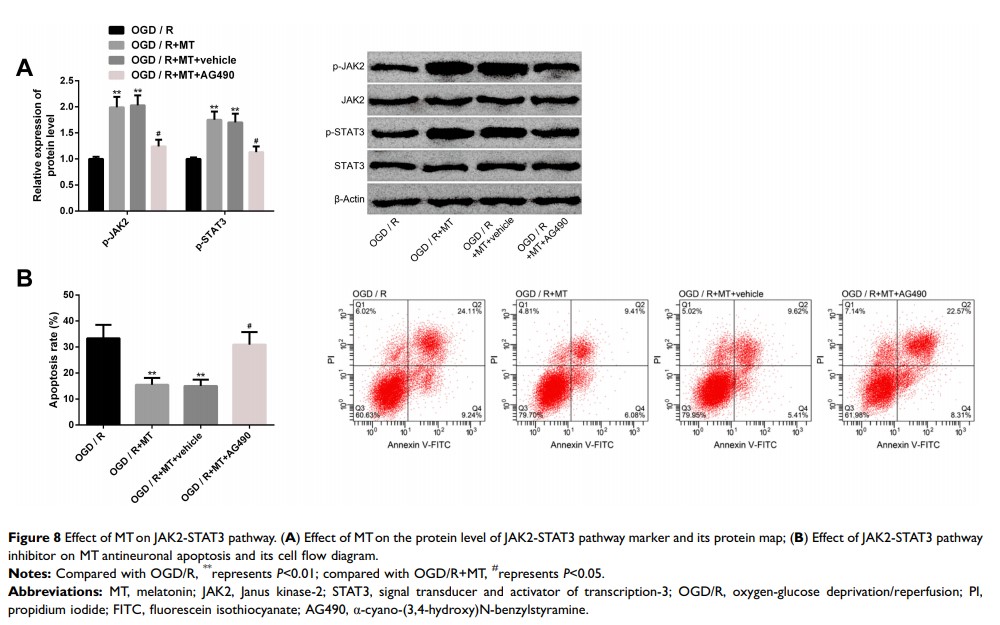
Results: MT pretreatment can significantly reduce neurological deficit score and neuronal apoptosis, inhibit CIRI autophagy, inflammation and oxidative stress in vivo and in vitro, reduce LC3II/LC3I, TNF-α, IL-6, MDA and increase P62, IL-10, GSHPx, SOD. Further analysis identifies that downregulating miR-26a-5p or upregulating NRSF can eliminate the protective effect of MT, and NRSF is the direct target of miR-26a-5p. The protective effect of MT can also be eliminated under AG490 intervention.
Conclusion: MT plays a protective role by regulating miR-26a-5p-NRSF and JAK2-STAT3 pathway to improve CIRI autophagy, inflammation and oxidative stress.
Keywords: cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury, melatonin, miR-26a-5p, NRSF, JAK2-STAT3