108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-100 rs1834306 A> G 增加了华南儿童患先天性巨结肠症的风险
Authors Zhu Y, Lin A, Zheng Y, Xie X, He Q, Zhong W
Received 2 June 2020
Accepted for publication 27 July 2020
Published 10 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 283—288
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PGPM.S265730
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Martin Bluth
Background: Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) is a rare congenital gastrointestinal disease characterized by the absence of intestinal submucosal and myometrial ganglion cells. Recently, researches indicated that miR-100 regulated the growth, differentiation and apoptosis of neurons, and affected the functions of HSCR-associated pathways. While miR-100 rs1834306 A>G polymorphism was shown to modify the susceptibility to tumors, the association between this polymorphism and HSCR susceptibility is still unknown.
Methods: This was a case–control study consisting of 1470 HSCR cases and 1473 controls from southern China. DNA was genotyped by TaqMan real-time PCR. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used as statistical indicators.
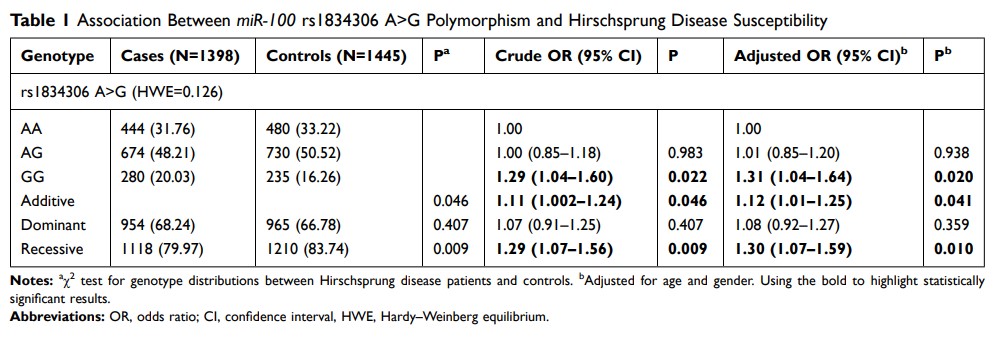
Results: We found that miR-100 rs1834306 G allele and GG genotype significantly increased HSCR susceptibility (GG vs AA: adjusted OR=1.31, 95% CI=1.04– 1.64, P =0.020; G vs A: adjusted OR=1.12, 95% CI=1.01– 1.25, P =0.041; GG vs AA/AG: adjusted OR=1.30, 95% CI=1.07– 1.59, P =0.010). In the stratified analysis, miR-100 rs1834306 GG genotype carriers had higher risk to develop HSCR in all clinical subtypes when compared with those with AA/AG genotypes, and OR was rising with HSCR aggravation (SHSCR: adjusted OR=1.28, 95% CI=1.03– 1.59, P =0.029; LHSCR: adjusted OR=1.48, 95% CI=1.06– 2.07, P =0.020; TCA: adjusted OR=2.12, 95% CI=1.22– 3.69, P =0.008).
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that miR-100 rs1834306 A>G polymorphism was associated with increased HSCR susceptibility in southern Chinese children. Furthermore, miR-100 rs1834306 GG genotype had a greater genetic pathopoiesis in severe HSCR.
Keywords: Hirschsprung disease, miR-100 , polymorphism, susceptibility