108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

与中国女性乳腺癌风险相关的胰岛素和胰岛素样生长因子轴生物标志物
Authors Zhu Y, Wang T, Wu J, Huang O, Zhu L, He J, Li Y, Chen W, Chen X, Shen K
Received 15 April 2020
Accepted for publication 10 July 2020
Published 11 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 8027—8036
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S258357
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: The interplay between biomarkers of insulin and the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis in the context of breast cancer risk is unclear.
Methods: We measured the concentrations of insulin, C-peptide, IGF1, and IGF binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) and calculated the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) index and the IGF1/IGFBP3 ratio among 2536 patients with breast cancer and 2528 patients with benign breast disease recruited from Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai, China, between 2012 and 2017.
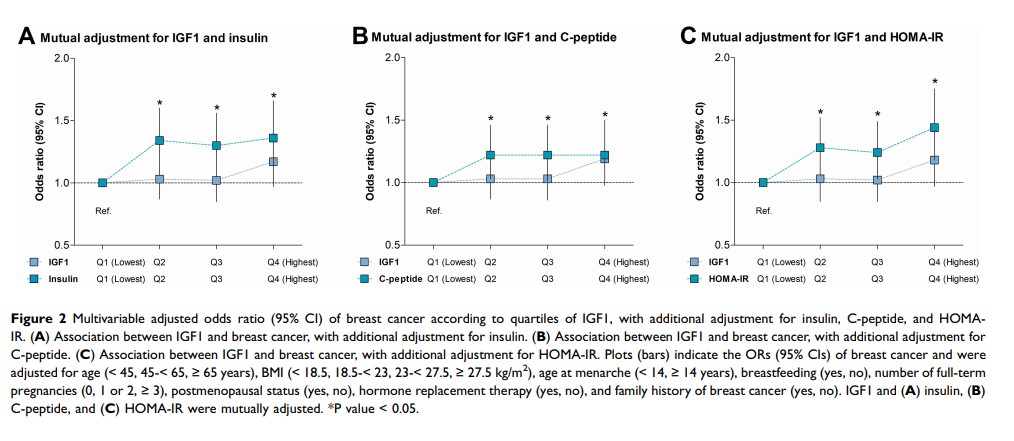
Results: Multivariable-adjusted odds ratios (ORs) for breast cancer associated with the highest quartiles versus the lowest quartiles of insulin and IGF factors were 1.45 (95% CI, 1.20– 1.75) for insulin, 1.32 (1.08– 1.60) for C-peptide, 1.53 (1.26– 1.85) for HOMA-IR, and 1.27 (1.05– 1.53) for IGF1; these associations did not differ substantially across stratifications of age, body mass index, age at menarche, or menopausal status (all P for interaction > 0.05). In the joint analysis, the highest quartile of IGF1 was associated with the greatest risk of breast cancer in the highest quartiles of insulin (OR, 1.77; 95% CI, 1.29– 2.44), C-peptide (1.60; 1.17– 2.20), and HOMA-IR (1.90; 1.38– 2.62), compared with the risks associated with the combination of the lowest quartiles of IGF1 and each insulin factor. In stratification analysis, the positive association between IGF1 and breast cancer was stronger in the highest quartiles of insulin (P[interaction] = 0.29), C-peptide (P[interaction] = 0.020), and HOMA-IR (P[interaction] = 0.075).
Conclusion: Our findings indicate effect modifications of insulin, C-peptide, and insulin resistance on the relationship between IGF1 and breast cancer risk in Chinese women.
Keywords: insulin, insulin-like growth factor 1, C-peptide, insulin resistance, breast cancer