108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

低强度超声可增强 Hsp90 抑制剂 SNX-2112 对舌鳞状细胞癌的抗肿瘤发生效应
Authors Nan C, Zheng Y, Fan H, Sun H, Huang S, Li N
Received 27 May 2020
Accepted for publication 24 July 2020
Published 12 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 7907—7919
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S262174
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos E Vigil
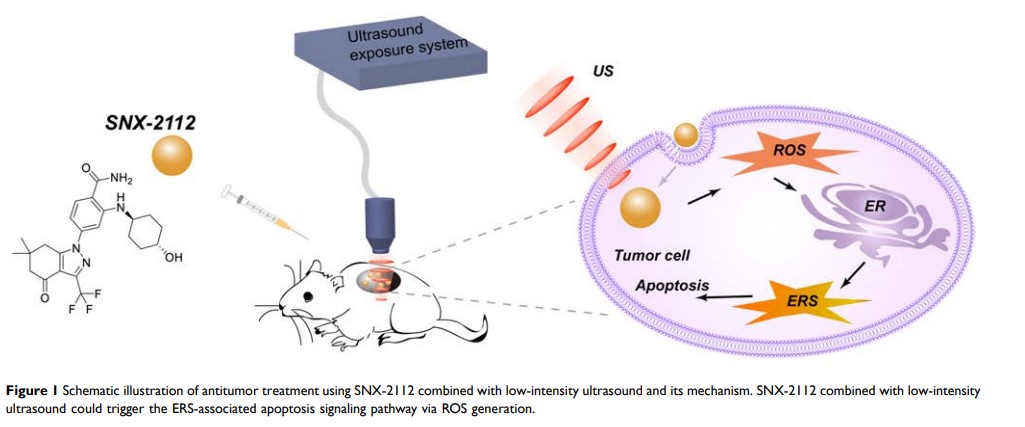
Purpose: The novel Hsp90 inhibitor SNX-2112 showed broad antitumor activity. However, it was still necessary to optimize the therapeutic dosage of SNX-2112 applied on tumors to obtain effective therapy with minimal dose to reduce toxicity. We investigated the role of low-intensity US in promoting antitumorigenic effect of low doses of SNX-2112 on tongue squamous cell carcinoma.
Methods: Cell viability was measured using CCK-8 assay or staining with Calcein AM/PI. Relative cumulative levels of SNX-2112 in cells were detected using high-performance liquid chromatography. The production of ROS was analyzed using fluorescence microscope and flow cytometer. Cellular apoptosis was detected using flow cytometer. The expression levels of proteins of the ERS-associated apoptosis signaling pathway were detected using Western blotting analysis. The efficacy and biosafety of SNX-2112 were also investigated in a mouse xenograft model.
Results: Low-intensity US combined with SNX-2112 exhibited significant antitumor effect, increased the absorption of SNX-2112 by cells even with a low dose, enhanced ROS generation and apoptosis. The combination regimen also inhibited the protein expression of Hsp90 and triggered apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) by enhancing PERK, CHOP and Bax protein levels, while downregulating the level of Bcl-2. Additionally, N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), ROS scavenger, was able to reverse these results. Low-intensity US combined with SNX-2112 significantly inhibited tumor growth, prolonged survival of mice, decreased proliferation and promoted apoptosis with no visible damage or abnormalities in major organs in the mouse xenograft model with tongue squamous cell carcinoma.
Conclusion: The antitumor effects of SNX-2112 were enhanced by low-intensity US. The most probable mechanism was that US sonoporation induced more SNX-2112 delivery to the cells and enhanced ROS production, triggering the ERS-associated apoptosis signaling pathway. Therefore, low-intensity US may increase the efficiency of conventional chemotherapy and reduce the dosage of SNX-2112 required and its side effects.
Keywords: low-intensity ultrasound, SNX-2112, tongue squamous cell carcinoma, reactive oxygen species, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis