108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

负载阿霉素和依地福新的脂质-聚合物杂化纳米粒子对耐药性骨肉瘤的协同抗癌作用
Authors Yang P, Zhang L, Wang T, Liu Q, Wang J, Wang Y, Tu Z, Lin F
Received 30 April 2020
Accepted for publication 13 July 2020
Published 12 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 8055—8067
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S259428
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Introduction: The failure of chemotherapy in osteosarcoma results in drug resistance and acute side effects in the body.
Methods: In this study, we have prepared a novel folate receptor-targeted doxorubicin (DOX) and edelfosine (EDL)-loaded lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticle (DE-FPLN) to enhance the anticancer efficacy in osteosarcoma. The nanoparticles were thoroughly characterized for in vitro biological assays followed by detailed antitumor efficacy analysis and toxicity analysis in a xenograft model.
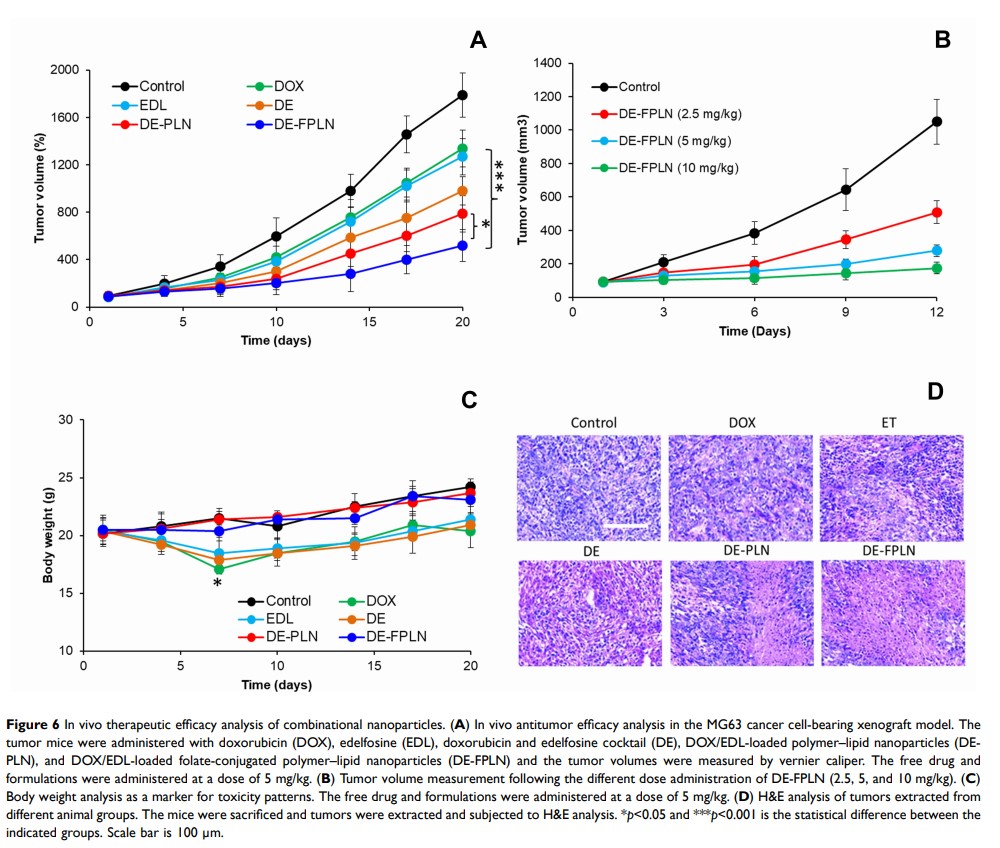
Results: The dual drug-loaded nanoparticles showed a nanosized morphology and physiological stability. The targeted nanoparticles showed enhanced cellular internalization and subcellular distribution in MG63 cancer cells compared to that of non-targeted nanoparticles. Among many ratios of DOX and EDL, 1:1 ratiometric combinations of drugs were observed to be highly synergistic in killing the cancer cells. MTT assay and caspase-3/7 activity assay clearly showed the superior anticancer efficacy of DE-FPLN formulations in inducing the cancer cell death. In vitro results indicate that the co-administration of two drugs in a folic acid-targeted nanoparticle could potentially induce the apoptosis and cell death. In vivo results displayed the potency of tumor cell killing and significant suppression of tumor growth without any detectable side effects.
Conclusion: The lipid–polymer hybrid nanocarriers with multiple properties of high drug loading, sequential and ratiometric drug release, improved physiological stability, prolonged blood circulation, and tumor-specific targeting are promising for the delivery of multiple drugs in the treatment of osteosarcoma.
Keywords: osteosarcoma, doxorubicin, edelfosine, nanoparticles, apoptosis, combination chemotherapy