108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

URM1 通过 JNK 信号通路促进肝细胞癌的肿瘤生长并抑制细胞凋亡
Authors Cheng X, Zhang Y, Song F, Song F, Gao C, Liang X, Wang F, Chen Z
Received 23 April 2020
Accepted for publication 15 July 2020
Published 12 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 8011—8025
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S258843
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjeev Srivastava
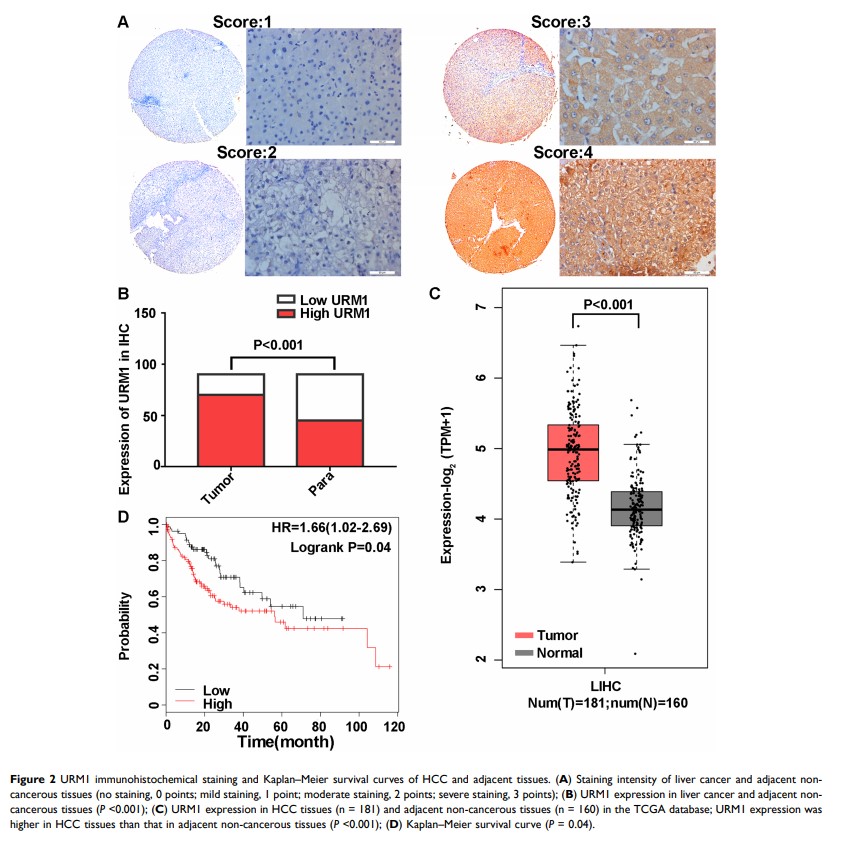
Objective: Ubiquitin-related modifier 1 (URM1) is a member of the ubiquitin-like regulator family, which acts as a post-translational protein modifier in the oxidative emergency response mechanism. Previous studies have shown that URM1 may be involved in the process of apoptosis and may play a role in JNK signaling pathway. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role and possible mechanism of URM1 in HCC progression.
Patients and Methods: Expression of URM1 was determined in 90 pairs of matched liver cancer and adjacent non-cancerous tissues by immunohistochemistry. The impacts of URM1 on HCC cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion capacities were verified by CCK-8, colony formation, TUNEL staining, wound healing assay and transwell, respectively. Then, the effect of URM1 on subcutaneous tumor formation in vitro was explored by nude mouse xenograft model of liver cancer. Finally, the expression of apoptosis-related proteins was analyzed in URM1 knockdown samples by Western blotting.
Results: In this study, compared with paired adjacent non-cancerous tissues, the expression of URM1 was higher in liver cancer tissues (P < 0.01). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed that high URM1 expression was significantly associated with poor prognosis (P < 0.05). Moreover, URM1 knockdown inhibited liver cancer cell proliferation and migration. Furthermore, URM1 knockdown promoted apoptosis of liver cancer cells. At the same time, URM1 knockdown inhibited tumor growth in nude mouse xenograft model of liver cancer. In addition, URM1 knockdown downregulated the expression of the apoptosis-related factors JNK1/2 and TP53 and upregulated the phosphorylation of JNK1/2 and P53.
Conclusion: In summary, our results suggested that URM1 expression is increased in liver cancer tissues, and URM1 knockdown inhibits the proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells and accelerates apoptosis. High URM1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, URM1, proliferation, migration, apoptosis, JNK signaling pathway