108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国重庆市学龄前儿童的行为问题:现状及影响因素
Authors Yu Y, Wang T, Liang J, Yang C, Wang H, Zhao X, Zhang J, Liu W
Received 3 June 2020
Accepted for publication 28 July 2020
Published 13 August 2020 Volume 2020:13 Pages 1149—1160
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S263155
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Marco Carotenuto
Introduction: Behavioural problems in pre-school children are closely related to their mental health. Such problems include attention deficit, personality disorder, overdependency, poor adaptability and conduct problems.
Methods: From December 2018 to January 2019, we conducted a cross-sectional survey of parents of pre-schoolers. The survey covered sixteen kindergartens in six districts of Chongqing, China. A total of 2200 participants participated in the survey, and 1895 questionnaires were returned. After screening, 1496 valid questionnaires were compiled in the data analysis (n=1496).
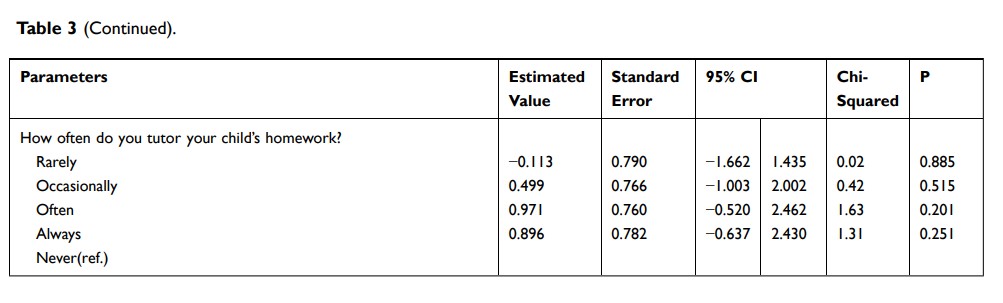
Results: Analysis of the maximum likelihood estimation revealed that age, preterm birth, household income, amount of daily interaction with parents, and scolding frequency affected behavioural problems in the pre-schoolers. Behavioural problems tend to be attenuated as children grow. Preterm children had a higher probability of developing behavioural problems than did non-preterm children. Children from families with monthly household incomes between $1130–$1695 USD and $1696–$2260 USD were more prone to developing behavioural problems. Children whose parents spent less time interacting with them (39.26% of parents interacted with children less than 1 hour per day) and children who were scolded more often had greater behavioural problems (13.44% of parents often scolded their children).
Discussion: This study was conducted to evaluate the influence of parenting methods on pre-school children and the education provided by parents on their pre-school children’s behavioural problems to provide insights for Chinese parents and mental health professionals to improve treatment of behavioural problems.
Keywords: behavioural problems, pre-school children, parental education, China