108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

帕金森氏病中衍生自人脂肪组织的间充质干细胞:抑制辅助性 T 细胞 17 的分化及调节免疫平衡,以达到调节性 T 细胞的表型
Authors Bi Y, Lin X, Liang H, Yang D, Zhang X, Ke J, Xiao J, Chen Z, Chen W, Zhang X, Wang S, Liu CF
Received 3 May 2020
Accepted for publication 28 July 2020
Published 13 August 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 1383—1391
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S259762
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Background: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder displaying a typical neuroinflammation pathology that may result from an imbalance between regulatory T cells (Treg) and T helper 17 (Th17) cells. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Ad-MSCs) exert immunomodulatory effects by inhibiting effector T cell responses and have been used to treat diverse immune disorders. We aimed to investigate the modulating effect of human Ad-MSCs on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of patients with PD, focusing on differentiation into Th17 and Treg cells.
Methods: We isolated human peripheral blood CD4+T cells and co-cultured them with Ad-MSCs at a ratio of 4:1 under either Th17 or Treg cell polarizing conditions for 4 days to detect the proportions of IL-17-producing CD4+T (Th17) and CD4+CD25+Foxp3+regulatory T (Treg) cells by flow cytometry. We also determined the mRNA expression levels of the retinoid-related orphan nuclear receptor (RORγt) transcription factor and those of interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R), interleukin-23 receptor (IL-23R), leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), and LIF receptor (LIFR) by quantitative reverse transcription PCR. We detected levels of cytokines in the supernatant (including LIF, IL-6, IL-23, IL-10, and TGF-β) using ELISA.
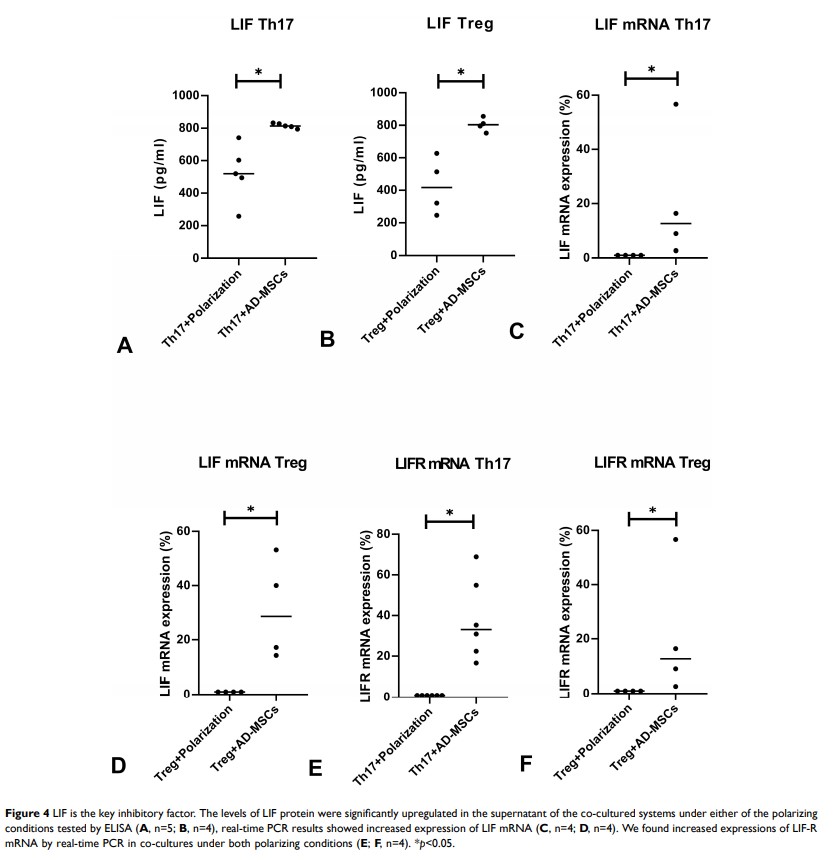
Results: Our results showed that Ad-MSCs specifically inhibited the differentiation of PBMCs of patients with PD into IL-17-producing CD4+T cells by decreasing expressions of IL-6R, IL-23R, and RORγt (the key transcription factor for Th17 cells). Moreover, Ad-MSCs induced a functional CD4+CD25+Foxp3+T regulatory cell phenotype as evidenced by the secretion of IL-10. The levels of IL-6, IL-23, and TGF-β remained constant after co-culture under either the Th17 or the Treg cell polarizing condition. In addition, levels of LIF protein and its receptor mRNA were significantly increased under both polarizing conditions.
Conclusion: The present in vitro study found that Ad-MSCs from healthy participants were able to correct the imbalance between Th17 and Treg found in PBMCs of PD patients, which were correlated with an increase in LIF secretion and a decrease in expression of IL-6R, IL-23R, and RORγt. These findings should be confirmed by in vivo experiments.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease, adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells, CD4+T cell, T helper 17 cell, T regulatory cell, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, leukemia inhibitory factor