108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

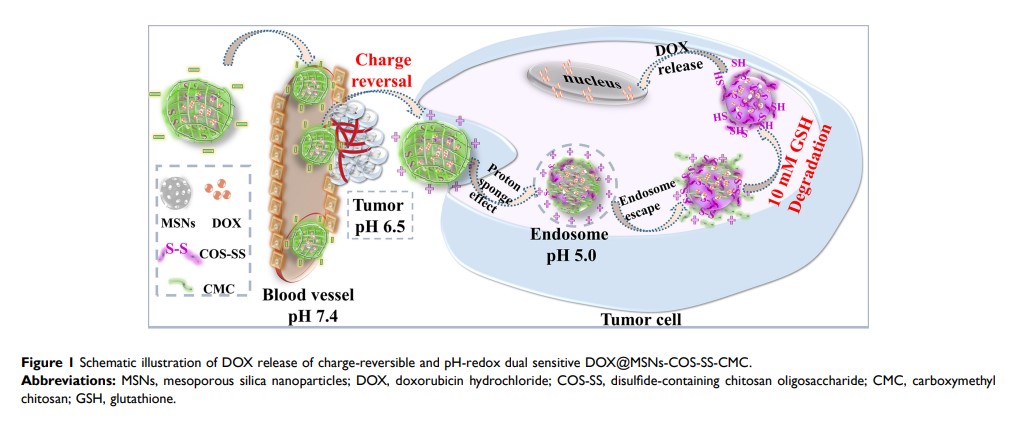
电荷逆转的级联靶向和二硫键屏蔽用于多级敏感的 MSNs-COS-SS-CMC 的有效 DOX 传递
Authors Cui L, Liu W, Liu H, Qin Q, Wu S, He S, Zhang Z, Pang X, Zhu C
Received 6 March 2020
Accepted for publication 8 July 2020
Published 17 August 2020 Volume 2020:15 Pages 6153—6165
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S252769
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single anonymous peer review
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Thomas Webster
Background: Although pH and redox sensitiveness have been extensively investigated to improve therapeutic efficiency, the effect of disulfide bonds location and pH-triggered charge-reversal on cascade-targeting still need to be further evaluated in cancer treatment with multi-responsive nanoparticles.
Purpose: The aim of this study was to design multi-responsive DOX@MSNs-COS-NN-CMC, DOX@MSNs-COS-SS-CMC and DOX@MSNs-COS-CMC-SS and systematically investigate the effects of disulfide bonds location and charge-reversal on the cancer cell specificity, endocytosis mechanisms and antitumor efficiency.
Results: In vitro drug release rate of DOX@MSNs-COS-SS-CMC in tumor environments was 7-fold higher than that under normal physiological conditions after 200 h. Furthermore, the fluorescence intensity of DOX@MSNs-COS-SS-CMC and DOX@MSNs-COS-CMC-SS was 1.9-fold and 1.3-fold higher than free DOX at pH 6.5 and 10 mM GSH. In addition, vesicular transport might be a factor that affects the uptake efficiency of DOX@MSNs-COS-SS-CMC and DOX@MSNs-COS-CMC-SS. The clathrin-mediated endocytosis and endosomal escape of DOX@MSNs-COS-SS-CMC enhanced cellular internalization and preserved highly controllable drug release into the perinuclear of HeLa cells. DOX@MSNs-COS-SS-CMC exhibited a synergistic chemotherapy in preeminent tumor inhibition and less side effects of cardiotoxicity.
Conclusion: The cascade-targeting of charge-reversal and disulfide bonds shielding would be a highly personalized strategy for cervical cancer treatment.
Keywords: disulfide bonds, pH-triggered charge-reversal, redox sensitive, chitosan oligosaccharide, human cervical carcinoma therapy